Diversity and structure of the methanogenic community in anoxic rice paddy soil microcosms as examined by cultivation and direct 16S rRNA gene sequence retrieval
- PMID: 9501436
- PMCID: PMC106352
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.3.960-969.1998
Diversity and structure of the methanogenic community in anoxic rice paddy soil microcosms as examined by cultivation and direct 16S rRNA gene sequence retrieval
Abstract
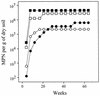
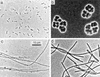
A dual approach consisting of cultivation and molecular retrieval of partial archaeal 16S rRNA genes was carried out to characterize the diversity and structure of the methanogenic community inhabiting the anoxic bulk soil of flooded rice microcosms. The molecular approach identified four groups of known methanogens. Three environmental sequences clustered with Methanobacterium bryantii and Methanobacterium formicicum, six were closely related but not identical to those of strains of Methanosaeta concilii, two grouped with members of the genus Methanosarcina, and two were related to the methanogenic endosymbiont of Plagiopyla nasuta. The cultivation approach via most-probable-number counts with a subsample of the same soil as an inoculum yielded cell numbers of up to 10(7) per g of dry soil for the H2-CO2-utilizing methanogens and of up to 10(6) for the acetate-utilizing methanogens. Strain VeH52, isolated from the terminal positive dilution on H2-CO2, grouped within the phylogenetic radiation characterized by M. bryantii and M. formicicum and the environmental sequences of the Methanobacterium-like group. A consortium of two distinct methanogens grew in the terminal positive culture on acetate. These two organisms showed absolute 16S rRNA gene identities with environmental sequences of the novel Methanosaeta-like group and the Methanobacterium-like group. Methanosarcina spp. were identified only in the less-dilute levels of the same dilution series on acetate. These data correlate well with acetate concentrations of about 11 microM in the pore water of this rice paddy soil. These concentrations are too low for the growth of known Methanosarcina spp. but are at the acetate utilization threshold of Methanosaeta spp. Thus, our data indicated Methanosaeta spp. and Methanobacterium spp. to be the dominant methanogenic groups in the anoxic rice soil, whereas Methanosarcina spp. appeared to be less abundant.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vertical distribution of methanogens in the anoxic sediment of Rotsee (Switzerland).Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999 Jun;65(6):2402-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.6.2402-2408.1999. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10347020 Free PMC article.
-
Methanogenic archaea and CO2-dependent methanogenesis on washed rice roots.Environ Microbiol. 1999 Apr;1(2):159-66. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-2920.1999.00019.x. Environ Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 11207731
-
Comparative phylogenetic assignment of environmental sequences of genes encoding 16S rRNA and numerically abundant culturable bacteria from an anoxic rice paddy soil.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999 Nov;65(11):5050-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.11.5050-5058.1999. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10543822 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and identification of numerically abundant culturable bacteria from the anoxic bulk soil of rice paddy microcosms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999 Nov;65(11):5042-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.11.5042-5049.1999. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10543821 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of temperature on structure and function of the methanogenic archaeal community in an anoxic rice field soil.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999 Jun;65(6):2341-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.6.2341-2349.1999. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10347011 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Methanogenic Community Characteristics and Its Influencing Factors in Reservoir Sediments on the Northeastern Qinghai Plateau.Biology (Basel). 2024 Aug 14;13(8):615. doi: 10.3390/biology13080615. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194553 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquity of methanogenic archaea in the trunk of coniferous and broadleaved tree species in a mountain forest.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2024 Jul 26;117(1):107. doi: 10.1007/s10482-024-02004-5. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2024. PMID: 39060562
-
Isolation of a methyl-reducing methanogen outside the Euryarchaeota.Nature. 2024 Aug;632(8027):1124-1130. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07728-y. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39048829
-
Impacts of Groundwater Pumping on Subterranean Microbial Communities in a Deep Aquifer Associated with an Accretionary Prism.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 28;12(4):679. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040679. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674625 Free PMC article.
-
Time-shifted expression of acetoclastic and methylotrophic methanogenesis by a single Methanosarcina genomospecies predominates the methanogen dynamics in Philippine rice field soil.Microbiome. 2024 Feb 26;12(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01739-z. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 38409166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achtnich C, Schuhmann A, Wind T, Conrad R. Role of interspecies H2 transfer to sulfate and ferric iron-reducing bacteria in acetate consumption in anoxic paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 1995;16:61–70.
-
- Asakawa S, Akagawa-Matsushita M, Morii H, Koga Y, Hayano K. Characterization of Methanosarcina mazeii TMA isolated from a paddy field soil. Curr Microbiol. 1995;31:34–38.
-
- Asakawa S, Morii H, Akagawa-Matsushita M, Koga Y, Hayano K. Characterization of Methanobrevibacter arboriphilicus SA isolated from a paddy field soil and DNA-DNA hybridization among M. arboriphilicus strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1993;43:683–686.
-
- Beliaeff B, Mary J Y. The “most probable number” estimate and its confidence limits. Water Res. 1993;27:799–805.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

