Hidden mechanical weaknesses within lava domes provided by buried high-porosity hydrothermal alteration zones
- PMID: 35217684
- PMCID: PMC8881499
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-06765-9
Hidden mechanical weaknesses within lava domes provided by buried high-porosity hydrothermal alteration zones
Abstract
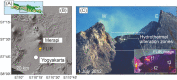
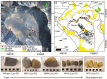
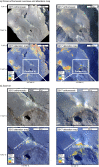
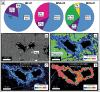
Catastrophic lava dome collapse is considered an unpredictable volcanic hazard because the physical properties, stress conditions, and internal structure of lava domes are not well understood and can change rapidly through time. To explain the locations of dome instabilities at Merapi volcano, Indonesia, we combined geochemical and mineralogical analyses, rock physical property measurements, drone-based photogrammetry, and geoinformatics. We show that a horseshoe-shaped alteration zone that formed in 2014 was subsequently buried by renewed lava extrusion in 2018. Drone data, as well as geomechanical, mineralogical, and oxygen isotope data suggest that this zone is characterized by high-porosity hydrothermally altered materials that are mechanically weak. We additionally show that the new lava dome is currently collapsing along this now-hidden weak alteration zone, highlighting that a detailed understanding of dome architecture, made possible using the monitoring techniques employed here, is essential for assessing hazards associated with dome and edifice failure at volcanoes worldwide.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Muon radiography and deformation analysis of the lava dome formed by the 1944 eruption of Usu, Hokkaido--contact between high-energy physics and volcano physics--.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2008;84(4):107-16. doi: 10.2183/pjab.84.107. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18941290 Free PMC article.
-
What factors control superficial lava dome explosivity?Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 30;5:14551. doi: 10.1038/srep14551. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26420069 Free PMC article.
-
Volcano electrical tomography unveils edifice collapse hazard linked to hydrothermal system structure and dynamics.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 26;6:29899. doi: 10.1038/srep29899. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27457494 Free PMC article.
-
Volcano-ice interaction as a microbial habitat on Earth and Mars.Astrobiology. 2011 Sep;11(7):695-710. doi: 10.1089/ast.2010.0550. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Astrobiology. 2011. PMID: 21877914 Review.
-
Geotourism and volcanoes: health hazards facing tourists at volcanic and geothermal destinations.Travel Med Infect Dis. 2009 Sep;7(5):257-61. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2009.06.002. Epub 2009 Jul 5. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19747658 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-failure deformation mode switching in volcanic rock.R Soc Open Sci. 2024 Aug 28;11(8):240792. doi: 10.1098/rsos.240792. eCollection 2024 Aug. R Soc Open Sci. 2024. PMID: 39205996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Norton GE, et al. Pyroclastic flow and explosive activity at Soufrière Hills Volcano, Montserrat, during a period of virtually no magma extrusion (March 1998 to November 1999) Geol. Soc. Lond. Memoirs. 2002;21:467–481. doi: 10.1144/GSL.MEM.2002.021.01.21. - DOI
-
- Yamamoto T, Takarada S, Suto S. Pyroclastic flows from the 1991 eruption of Unzen volcano Japan. Bull. Volcanol. 1993;55:166–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00301514. - DOI
-
- Watters RJ, Zimbelman DR, Bowman SD, Crowley JK. Rock mass strength assessment and significance to edifice stability, Mount Rainier and Mount Hood Cascade Range Volcanoes. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2000;157:957–976. doi: 10.1007/s000240050012. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

