Data on the design and operation of drones by both individuals and teams
- PMID: 33855142
- PMCID: PMC8027539
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2021.107008
Data on the design and operation of drones by both individuals and teams
Abstract
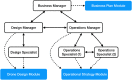
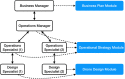
Human subject experiments are performed to assess the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) agents on distributed human design teams and individual human designers. In the team experiment, participants in teams of six develop and operate a drone fleet to deliver parcels routed to multiple locations of a target market. Among the design teams in the experiment, half of the design teams are human-only teams with no available AI agent. The other half of the design teams, designated as hybrid teams, have drone design and operation AI agents to advise them. Halfway through the team experiment, team structure is changed unexpectedly, requiring participants to adapt to the change. In the individual experiment, participants develop drones based on given design specifications, either on their own or with the availability of a drone design AI agent to advise them. During these experiments, participants configure, test, and share their designs and communicate with their teammates through an online research platform. The platform collects a step-by-step log of the actions made by participants. This article contains data sets collected from 44 teams (264 participants) in the team experiment and 73 participants in the individual experiment. These data sets can be used for behavioral analysis, sequence-based analysis, and natural language processing.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Collaborative design; Design teams; Engineering design; Human–computer interaction; Team agility; Team structures.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships which have or could be perceived to have influenced the work reported in this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Data on the Human Versus artificial intelligence process management experiment.Data Brief. 2022 Feb 8;41:107917. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.107917. eCollection 2022 Apr. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 35242909 Free PMC article.
-
Data on the design of truss structures by teams of engineering students.Data Brief. 2018 Mar 8;18:160-163. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.02.078. eCollection 2018 Jun. Data Brief. 2018. PMID: 29896506 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Ethical AI: Empirically Investigating Dimensions of AI Ethics, Trust Repair, and Performance in Human-AI Teaming.Hum Factors. 2024 Apr;66(4):1037-1055. doi: 10.1177/00187208221116952. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Hum Factors. 2024. PMID: 35938319
-
A developmental and psychoeducational approach to reducing conflict and abuse in little league and youth sports. The sport psychiatrist's role.Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 1998 Oct;7(4):891-918. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 1998. PMID: 9894049 Review.
-
Secondary analysis and literature review of community rehabilitation and intermediate care: an information resource.Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Jan. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Jan. PMID: 25642549 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Data on the Human Versus artificial intelligence process management experiment.Data Brief. 2022 Feb 8;41:107917. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.107917. eCollection 2022 Apr. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 35242909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song B., Soria Zurita N.F., Zhang G., Stump G., Balon C., Miller S.W., Yukish M., Cagan J., McComb C. Proceedings of the Design Society: Design Conference. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press; 2020. Toward hybrid teams: a platform to understand human-computer collaboration during the design of complex engineered systems; pp. 1551–1560. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

