Imaging unlabeled proteins on DNA with super-resolution
- PMID: 32016413
- PMCID: PMC7102996
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa061
Imaging unlabeled proteins on DNA with super-resolution
Abstract
Fluorescence microscopy is invaluable to a range of biomolecular analysis approaches. The required labeling of proteins of interest, however, can be challenging and potentially perturb biomolecular functionality as well as cause imaging artefacts and photo bleaching issues. Here, we introduce inverse (super-resolution) imaging of unlabeled proteins bound to DNA. In this new method, we use DNA-binding fluorophores that transiently label bare DNA but not protein-bound DNA. In addition to demonstrating diffraction-limited inverse imaging, we show that inverse Binding-Activated Localization Microscopy or 'iBALM' can resolve biomolecular features smaller than the diffraction limit. The current detection limit is estimated to lie at features between 5 and 15 nm in size. Although the current image-acquisition times preclude super-resolving fast dynamics, we show that diffraction-limited inverse imaging can reveal molecular mobility at ∼0.2 s temporal resolution and that the method works both with DNA-intercalating and non-intercalating dyes. Our experiments show that such inverse imaging approaches are valuable additions to the single-molecule toolkit that relieve potential limitations posed by labeling.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
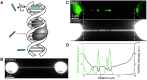
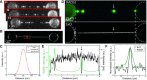
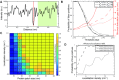
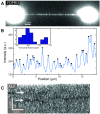
Similar articles
-
DNA and chromatin imaging with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy based on single-molecule localization.Biopolymers. 2011 May;95(5):290-7. doi: 10.1002/bip.21574. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Biopolymers. 2011. PMID: 21184489 Review.
-
Virtual-'light-sheet' single-molecule localisation microscopy enables quantitative optical sectioning for super-resolution imaging.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 17;10(4):e0125438. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125438. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25884495 Free PMC article.
-
Super-resolution microscopy with DNA-PAINT.Nat Protoc. 2017 Jun;12(6):1198-1228. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2017.024. Epub 2017 May 18. Nat Protoc. 2017. PMID: 28518172
-
Recent advances in super-resolution fluorescence imaging and its applications in biology.J Genet Genomics. 2013 Dec 20;40(12):583-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Nov 23. J Genet Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24377865 Review.
-
Example-Based Super-Resolution Fluorescence Microscopy.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 23;8(1):5700. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24033-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29686251 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Correlating fluorescence microscopy, optical and magnetic tweezers to study single chiral biopolymers such as DNA.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 29;15(1):2748. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47126-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38553446 Free PMC article.
-
Toward Sub-Diffraction Imaging of Single-DNA Molecule Sensors Based on Stochastic Switching Localization Microscopy.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Nov 21;20(22):6667. doi: 10.3390/s20226667. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33233370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virus self-assembly proceeds through contact-rich energy minima.Sci Adv. 2021 Nov 5;7(45):eabg0811. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abg0811. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34730996 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

