m6A in mRNA coding regions promotes translation via the RNA helicase-containing YTHDC2
- PMID: 31767846
- PMCID: PMC6877647
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-13317-9
m6A in mRNA coding regions promotes translation via the RNA helicase-containing YTHDC2
Abstract
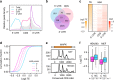
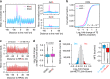
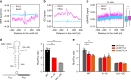
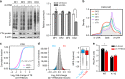
Dynamic mRNA modification in the form of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) adds considerable richness and sophistication to gene regulation. The m6A mark is asymmetrically distributed along mature mRNAs, with approximately 35% of m6A residues located within the coding region (CDS). It has been suggested that methylation in CDS slows down translation elongation. However, neither the decoding feature of endogenous mRNAs nor the physiological significance of CDS m6A has been clearly defined. Here, we found that CDS m6A leads to ribosome pausing in a codon-specific manner. Unexpectedly, removing CDS m6A from these transcripts results in a further decrease of translation. A systemic analysis of RNA structural datasets revealed that CDS m6A positively regulates translation by resolving mRNA secondary structures. We further demonstrate that the elongation-promoting effect of CDS methylation requires the RNA helicase-containing m6A reader YTHDC2. Our findings established the physiological significance of CDS methylation and uncovered non-overlapping function of m6A reader proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of m6A Transcripts by the 3'→5' RNA Helicase YTHDC2 Is Essential for a Successful Meiotic Program in the Mammalian Germline.Mol Cell. 2017 Oct 19;68(2):374-387.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.09.021. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 29033321
-
N6-methyladenosine modification of HCV RNA genome regulates cap-independent IRES-mediated translation via YTHDC2 recognition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 9;118(10):e2022024118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2022024118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33649237 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDC2 control of gametogenesis requires helicase activity but not m6A binding.Genes Dev. 2022 Feb 1;36(3-4):180-194. doi: 10.1101/gad.349190.121. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Genes Dev. 2022. PMID: 35058317 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted regulation of translation by the epitranscriptomic modification N6-methyladenosine.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Apr;56(2):137-148. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2020.1869174. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33412937 Review.
-
Protein Binding to Cis-Motifs in mRNAs Coding Sequence Is Common and Regulates Transcript Stability and the Rate of Translation.Cells. 2021 Oct 27;10(11):2910. doi: 10.3390/cells10112910. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831133 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of RNA structures and their roles in RNA functions.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Oct;25(10):784-801. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00748-6. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38926530 Review.
-
New horizons for the role of RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in hepatocellular carcinoma.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Jun;45(6):1130-1141. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01214-3. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38195693 Review.
-
Comprehensive Analysis and Functional Characteristics of Differential Expression of N6-Methyladenosine Methylation Modification in the Whole Transcriptome of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Oct 25;2022:4766992. doi: 10.1155/2022/4766992. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 36330380 Free PMC article.
-
Kdm4a is an activity downregulated barrier to generate engrams for memory separation.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 13;15(1):5887. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50218-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39003305 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine and RNA secondary structure affect transcript stability and protein abundance during systemic salt stress in Arabidopsis.Plant Direct. 2020 Jul 24;4(7):e00239. doi: 10.1002/pld3.239. eCollection 2020 Jul. Plant Direct. 2020. PMID: 32724893 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

