Takotsubo cardiomyopathy associated with Kounis syndrome: A clinical case of the "ATAK complex"
- PMID: 31440312
- PMCID: PMC6698252
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jccase.2019.03.007
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy associated with Kounis syndrome: A clinical case of the "ATAK complex"
Abstract
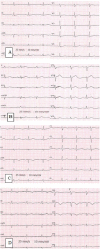
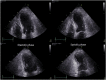
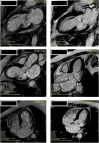
A 60-year-old female developed cardiac arrest after experiencing an anaphylactic shock during administration of plasma-expanders. An electrocardiogram registered after restoration of sinus rhythm showed mild ST-elevation in the anterior precordial leads and T waves changes followed by appearance of echocardiographic alterations of left ventricular apex kinesis. Coronary angiography revealed normal coronary arteries, and cardiovascular magnetic resonance confirmed apical ballooning with late gadolinium enhancement in the segments with abnormal contractility. This uncommon clinical case confirms how takotsubo and Kounis syndrome may converge in a single nosological entity, the so-called "ATAK complex" (Adrenaline, Tako-Tsubo, Anaphylaxis, and Kounis), with a specific management and prognostic implications. <Learning objective: The Kounis syndrome has a clinical presentation that poses a difficult differential diagnosis with takotsubo cardiomyopathy. Despite recent significant improvements in the understanding of these two clinical conditions, the pathogenesis of these two entities and, in particular, how they may converge into the clinical scenario of the "ATAK complex" remain to be clarified. We believe that this rare clinical case may help physicians in the correct identification and management of this frequently misdiagnosed clinical disease.>.
Keywords: ATAK complex; Anaphylaxis; Cardiac arrest; Kounis syndrome; Takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATAK Complex (Adrenaline, Takotsubo, Anaphylaxis, and Kounis Hypersensitivity-Associated Coronary Syndrome) after COVID-19 Vaccination and Review of the Literature.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;11(2):322. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020322. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851200 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenaline, Takotsubo, Anaphylaxis, and Kounis Syndrome (ATAK) Complex Unveiled: Integrating Takotsubo and Kounis Syndromes in the Context of Chemotherapy-Related Anaphylaxis.Cureus. 2024 Jan 29;16(1):e53145. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53145. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38420090 Free PMC article.
-
ATAK complex (adrenaline, takotsubo, anaphylaxis, and kounis hypersensitivity-associated coronary syndrome) related to latamoxef administration-a case report.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jul 22;11:1383903. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1383903. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39108674 Free PMC article.
-
Review: transient left ventricular apical ballooning, broken heart syndrome, ampulla cardiomyopathy, atypical apical ballooning, or Tako-Tsubo cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2007 Oct-Dec;8(4):289-92. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2007.02.001. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2007. PMID: 18053952 Review.
-
Management of Tako-tsubo syndrome.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2008 Feb;22(1):71-7. doi: 10.1007/s10557-007-6074-7. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2008. PMID: 18165891 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Variations in Etiology and Clinical Presentations of Kounis Syndrome Across Pediatric and Adult Populations: A Comprehensive Review.Cureus. 2024 Mar 16;16(3):e56249. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56249. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38623099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NButGT Reinforces the Beneficial Effects of Epinephrine on Cardiac Mitochondrial Respiration, Lactatemia and Cardiac Output in Experimental Anaphylactic Shock.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 14;25(6):3316. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063316. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542290 Free PMC article.
-
Kounis and Takotsubo, Two Syndromes Bound by Adrenaline: The "ATAK" Complex.Case Rep Cardiol. 2023 Sep 14;2023:7706104. doi: 10.1155/2023/7706104. eCollection 2023. Case Rep Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37744893 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial stunning secondary to erroneous administration of intravenous epinephrine.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2023 Mar 16;11:2050313X231159732. doi: 10.1177/2050313X231159732. eCollection 2023. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36950049 Free PMC article.
-
ATAK Complex (Adrenaline, Takotsubo, Anaphylaxis, and Kounis Hypersensitivity-Associated Coronary Syndrome) after COVID-19 Vaccination and Review of the Literature.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;11(2):322. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020322. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akashi Y.J., Nef H.M., Lyon A.R. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of Takotsubo syndrome. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015;12:387–397. - PubMed
-
- Pelliccia F., Kaski J.C., Crea F., Camici P.G. Pathophysiology of takotsubo syndrome. Circulation. 2017;135:2426–2441. - PubMed
-
- Abdelghany M., Subedi R., Shah S., Kozman H. Kounis syndrome: a review article on epidemiology, diagnostic findings, management and complications of allergic acute coronary syndrome. Int J Cardiol. 2017;232:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Templin C., Ghadri J.R., Diekmann J., Napp L.C., Bataiosu D.R., Jaguszewski M. Clinical features and outcomes of takotsubo (stress) cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:929–938. - PubMed
-
- Tsigkas G., Chouchoulis K., Theodoropoulos K., Kounis N.G., Alexopoulos D. Allergic reaction reveals a non-lethal late stent thrombosis. A new subtype of Kounis syndrome? Int J Cardiol. 2011;149:281–282. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

