Wearable step counting using a force myography-based ankle strap
- PMID: 31186946
- PMCID: PMC6453033
- DOI: 10.1177/2055668317746307
Wearable step counting using a force myography-based ankle strap
Abstract
Introduction: Step counting can be used to estimate the activity level of people in daily life; however, commercially available accelerometer-based step counters have shown inaccuracies in detection of low-speed walking steps (<2.2 km/h), and thus are not suitable for older adults who usually walk at low speeds. This proof-of-concept study explores the feasibility of using force myography recorded at the ankle to detect low-speed steps.
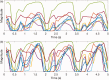
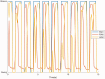
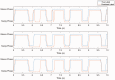
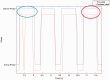
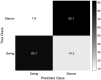
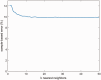
Methods: Eight young healthy participants walked on a treadmill at three speeds (1, 1.5, and 2.0 km/h) while their force myography signals were recorded at the ankle using a customized strap embedded with an array of eight force-sensing resistors. A K-nearest neighbour model was trained and tested with the recorded data. Additional three mainstream machine learning algorithms were also employed to evaluate the performance of force myography band as a pedometer.
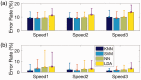
Results: Results showed a low error rate of the step detection (<1.5%) at all three walking speeds.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates not only the feasibility of the proposed approach but also the potential of the investigated technology to reliably monitor low-speed step counting.
Keywords: Force myography; force-sensing resistor band; gait analysis; older adults; pedometer.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Wearable Gait Phase Detection System Based on Force Myography Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Apr 21;18(4):1279. doi: 10.3390/s18041279. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29690532 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the ADAMO Care Watch for step counting in older adults.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 9;13(2):e0190753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190753. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29425196 Free PMC article.
-
Gait speed and step-count monitor accuracy in community-dwelling older adults.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008 Jan;40(1):59-64. doi: 10.1249/mss.0b013e318158b504. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008. PMID: 18091020
-
Validity and Reliability Evaluation of Four Commercial Activity Trackers' Step Counting Performance.Telemed J E Health. 2018 Sep;24(9):669-677. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2017.0264. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Telemed J E Health. 2018. PMID: 29303680
-
A New Force Myography-Based Approach for Continuous Estimation of Knee Joint Angle in Lower Limb Amputees and Able-Bodied Subjects.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021 Mar;25(3):701-710. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.2993697. Epub 2021 Mar 5. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021. PMID: 32396114
Cited by
-
A Wearable Gait Phase Detection System Based on Force Myography Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Apr 21;18(4):1279. doi: 10.3390/s18041279. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29690532 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting vertical ground reaction forces from 3D accelerometry using reservoir computers leads to accurate gait event detection.Front Sports Act Living. 2022 Oct 26;4:1037438. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2022.1037438. eCollection 2022. Front Sports Act Living. 2022. PMID: 36385782 Free PMC article.
-
Person Re-Identification Using Deep Modeling of Temporally Correlated Inertial Motion Patterns.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Feb 10;20(3):949. doi: 10.3390/s20030949. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32050728 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of EMG-, FMG-, and EIT-Based Biosensors and Relevant Human-Machine Interactivities and Biomedical Applications.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 12;12(7):516. doi: 10.3390/bios12070516. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Building Effective Machine Learning Models for Ankle Joint Power Estimation During Walking Using FMG Sensors.Front Neurorobot. 2022 Apr 1;16:836779. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2022.836779. eCollection 2022. Front Neurorobot. 2022. PMID: 35431852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CDC. Physical activity and health: a report of the surgeon general. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA, USA.
-
- Foster RC, Lanningham-Foster LM, Manohar C, et al. Precision and accuracy of an ankle-worn accelerometer-based pedometer in step counting and energy expenditure. Prev Med 2005; 41: 778–783. - PubMed
-
- Melanson EL, Knoll JR, Bell ML, et al. Commercially available pedometers: considerations for accurate step counting. Prev Med 2004; 39: 361–368. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

