Therapeutic role of miR-19a/19b in cardiac regeneration and protection from myocardial infarction
- PMID: 30996254
- PMCID: PMC6470165
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09530-1
Therapeutic role of miR-19a/19b in cardiac regeneration and protection from myocardial infarction
Abstract
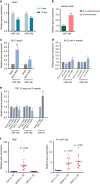
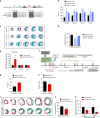
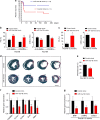
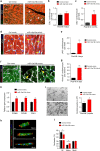
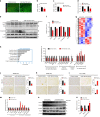
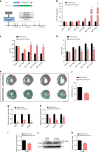
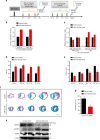
The primary cause of heart failure is the loss of cardiomyocytes in the diseased adult heart. Previously, we reported that the miR-17-92 cluster plays a key role in cardiomyocyte proliferation. Here, we report that expression of miR-19a/19b, members of the miR-17-92 cluster, is induced in heart failure patients. We show that intra-cardiac injection of miR-19a/19b mimics enhances cardiomyocyte proliferation and stimulates cardiac regeneration in response to myocardial infarction (MI) injury. miR-19a/19b protected the adult heart in two distinctive phases: an early phase immediately after MI and long-term protection. Genome-wide transcriptome analysis demonstrates that genes related to the immune response are repressed by miR-19a/19b. Using an adeno-associated virus approach, we validate that miR-19a/19b reduces MI-induced cardiac damage and protects cardiac function. Finally, we confirm the therapeutic potential of miR-19a/19b in protecting cardiac function by systemically delivering miR-19a/19b into mice post-MI. Our study establishes miR-19a/19b as potential therapeutic targets to treat heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-19b-1 reverses ischaemia-induced heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis and targeting Bcl2 l11/BIM.Heart Vessels. 2019 Jul;34(7):1221-1229. doi: 10.1007/s00380-018-01336-3. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Heart Vessels. 2019. PMID: 30607541
-
miR-19a/19b-loaded exosomes in combination with mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a preclinical model of myocardial infarction.Regen Med. 2020 Jun;15(6):1749-1759. doi: 10.2217/rme-2019-0136. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Regen Med. 2020. PMID: 32772806
-
The Therapeutic Effect of miRNA-19a/19b on Heart Failure in Mice and the Mechanism of Myocardial Regeneration and Repair.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2022 Feb 4;67(5):202-209. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2021.67.5.28. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2022. PMID: 35818252
-
Non-coding RNAs in endothelial cell signalling and hypoxia during cardiac regeneration.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020 Mar;1867(3):118515. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.07.010. Epub 2019 Jul 27. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31362011 Review.
-
Macro advances in microRNAs and myocardial regeneration.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2014 May;29(3):207-13. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000050. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24625819 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isoflurane and low-level carbon monoxide exposures increase expression of pro-survival miRNA in neonatal mouse heart.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021 May;26(3):541-548. doi: 10.1007/s12192-021-01199-0. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021. PMID: 33661504 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Targets for a Combination of Mechanical Unloading with Pharmacotherapy in Advanced Heart Failure.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 31;23(17):9886. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179886. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis in an angiotensin II-induced heart-on-a-chip disease model and extracellular vesicle screening.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 9;121(28):e2403581121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2403581121. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38968108 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulation Mechanisms and Clinical Application of MicroRNAs in Myocardial Infarction: A Review of the Recent 5 Years.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jan 17;8:809580. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.809580. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35111829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT3-miR-17/20 signalling axis plays a critical role in attenuating myocardial infarction following rapamycin treatment in diabetic mice.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Nov 1;116(13):2103-2115. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz315. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31738412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kennedy-Lydon, T. & Rosenthal, N. Cardiac regeneration: all work and no repair? Sci. Transl. Med. 9, eaad9019 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

