Optimized Clustering Algorithms for Large Wireless Sensor Networks: A Review
- PMID: 30650551
- PMCID: PMC6359437
- DOI: 10.3390/s19020322
Optimized Clustering Algorithms for Large Wireless Sensor Networks: A Review
Abstract
During the past few years, Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) have become widely used due to their large amount of applications. The use of WSNs is an imperative necessity for future revolutionary areas like ecological fields or smart cities in which more than hundreds or thousands of sensor nodes are deployed. In those large scale WSNs, hierarchical approaches improve the performance of the network and increase its lifetime. Hierarchy inside a WSN consists in cutting the whole network into sub-networks called clusters which are led by Cluster Heads. In spite of the advantages of the clustering on large WSNs, it remains a non-deterministic polynomial hard problem which is not solved efficiently by traditional clustering. The recent researches conducted on Machine Learning, Computational Intelligence, and WSNs bring out the optimized clustering algorithms for WSNs. These kinds of clustering are based on environmental behaviors and outperform the traditional clustering algorithms. However, due to the diversity of WSN applications, the choice of an appropriate paradigm for a clustering solution remains a problem. In this paper, we conduct a wide review of proposed optimized clustering solutions nowadays. In order to evaluate them, we consider 10 parameters. Based on these parameters, we propose a comparison of these optimized clustering approaches. From the analysis, we observe that centralized clustering solutions based on the Swarm Intelligence paradigm are more adapted for applications with low energy consumption, high data delivery rate, or high scalability than algorithms based on the other presented paradigms. Moreover, when an application does not need a large amount of nodes within a field, the Fuzzy Logic based solution are suitable.
Keywords: clustering; computational intelligence; large wireless sensor networks; machine learning; metaheuristic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
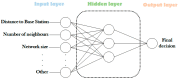
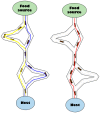
Similar articles
-
Software Defined Networking for Improved Wireless Sensor Network Management: A Survey.Sensors (Basel). 2017 May 4;17(5):1031. doi: 10.3390/s17051031. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28471390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GWLBC: Gray Wolf Optimization Based Load Balanced Clustering for Sustainable WSNs in Smart City Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 20;22(19):7113. doi: 10.3390/s22197113. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36236208 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Energy Efficient Clustering Protocol in Wireless Sensor Network Using Neuro-Fuzzy Approach.ScientificWorldJournal. 2016;2016:5063261. doi: 10.1155/2016/5063261. Epub 2016 Jan 3. ScientificWorldJournal. 2016. PMID: 26881269 Free PMC article.
-
DGTTSSA: Data Gathering Technique Based on Trust and Sparrow Search Algorithm for WSNs.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 8;23(12):5433. doi: 10.3390/s23125433. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37420600 Free PMC article.
-
A survey on clustering routing protocols in wireless sensor networks.Sensors (Basel). 2012;12(8):11113-53. doi: 10.3390/s120811113. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Sensors (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23112649 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Computer Vision-Based Roadside Occupation Surveillance System for Intelligent Transport in Smart Cities.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Apr 15;19(8):1796. doi: 10.3390/s19081796. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30991680 Free PMC article.
-
RRH Clustering Using Affinity Propagation Algorithm with Adaptive Thresholding and Greedy Merging in Cloud Radio Access Network.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jan 12;21(2):480. doi: 10.3390/s21020480. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33445462 Free PMC article.
-
Multi Swarm Optimization Based Clustering with Tabu Search in Wireless Sensor Network.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Feb 23;22(5):1736. doi: 10.3390/s22051736. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35270885 Free PMC article.
-
Covariance-Based Estimation for Clustered Sensor Networks Subject to Random Deception Attacks.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jul 14;19(14):3112. doi: 10.3390/s19143112. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31337128 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and prediction of athlete's anxiety state based on artificial intelligence.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023 May 25;9:e1322. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1322. eCollection 2023. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 37346592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dargie W., Poellabauer C. Fundamentals of Wireless Sensor Networks. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.; Chichester, UK: 2010.
-
- Yenke B.O., Wohwe Sambo D., Adamo Ado A.A., Gueroui A. MMEDD: Multithreading Model for an Efficient Data Delivery in wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Commun. Netw. Inf. Secur. 2016;8:179–186.
-
- Boukerche A., Ahmad M.Z., Turgut B., Turgut D. Algorithms and Protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2008. A Taxonomy of Routing Protocols in Sensor Networks; pp. 129–160.
-
- Sabor N., Sasaki S., Abo-Zahhad M., Ahmed S.M. A Comprehensive Survey on Hierarchical-Based Routing Protocols for Mobile Wireless Sensor Networks: Review, Taxonomy, and Future Directions. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017;2017:1–23. doi: 10.1155/2017/2818542. - DOI
-
- Avril F., Bernard T., Bui A., Sohier D. Clustering and communications scheduling in wsns using mixed integer linear programming. J. Commun. Netw. 2014;16:421–429. doi: 10.1109/JCN.2014.000072. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

