Determinants of early afterdepolarization properties in ventricular myocyte models
- PMID: 30475801
- PMCID: PMC6283611
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006382
Determinants of early afterdepolarization properties in ventricular myocyte models
Abstract
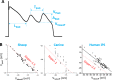
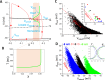
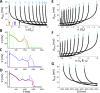
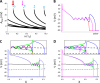
Early afterdepolarizations (EADs) are spontaneous depolarizations during the repolarization phase of an action potential in cardiac myocytes. It is widely known that EADs are promoted by increasing inward currents and/or decreasing outward currents, a condition called reduced repolarization reserve. Recent studies based on bifurcation theories show that EADs are caused by a dual Hopf-homoclinic bifurcation, bringing in further mechanistic insights into the genesis and dynamics of EADs. In this study, we investigated the EAD properties, such as the EAD amplitude, the inter-EAD interval, and the latency of the first EAD, and their major determinants. We first made predictions based on the bifurcation theory and then validated them in physiologically more detailed action potential models. These properties were investigated by varying one parameter at a time or using parameter sets randomly drawn from assigned intervals. The theoretical and simulation results were compared with experimental data from the literature. Our major findings are that the EAD amplitude and takeoff potential exhibit a negative linear correlation; the inter-EAD interval is insensitive to the maximum ionic current conductance but mainly determined by the kinetics of ICa,L and the dual Hopf-homoclinic bifurcation; and both inter-EAD interval and latency vary largely from model to model. Most of the model results generally agree with experimental observations in isolated ventricular myocytes. However, a major discrepancy between modeling results and experimental observations is that the inter-EAD intervals observed in experiments are mainly between 200 and 500 ms, irrespective of species, while those of the mathematical models exhibit a much wider range with some models exhibiting inter-EAD intervals less than 100 ms. Our simulations show that the cause of this discrepancy is likely due to the difference in ICa,L recovery properties in different mathematical models, which needs to be addressed in future action potential model development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamical mechanisms of phase-2 early afterdepolarizations in human ventricular myocytes: insights from bifurcation analyses of two mathematical models.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;312(1):H106-H127. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00115.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27836893
-
Dynamics of early afterdepolarization-mediated triggered activity in cardiac monolayers.Biophys J. 2012 Jun 20;102(12):2706-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.05.011. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 22735520 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-voltage coupling in the genesis of early and delayed afterdepolarizations in cardiac myocytes.Biophys J. 2015 Apr 21;108(8):1908-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.03.011. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 25902431 Free PMC article.
-
Early afterdepolarizations in cardiac myocytes: beyond reduced repolarization reserve.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Jul 1;99(1):6-15. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt104. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23619423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-to-cell electrical interactions during early and late repolarization.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006 May;17 Suppl 1:S8-S14. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2006.00379.x. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16686687 Review.
Cited by
-
Curvature-mediated source and sink effects on the genesis of premature ventricular complexes in long QT syndrome.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Jun 1;326(6):H1350-H1365. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00004.2024. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38551483
-
Dissecting the roles of calcium cycling and its coupling with voltage in the genesis of early afterdepolarizations in cardiac myocyte models.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Feb 28;20(2):e1011930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011930. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38416778 Free PMC article.
-
Computational modeling of cardiac electrophysiology and arrhythmogenesis: toward clinical translation.Physiol Rev. 2024 Jul 1;104(3):1265-1333. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00017.2023. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38153307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity and atrial fibrillation: a narrative review from arrhythmogenic mechanisms to clinical significance.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Jul 29;22(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01913-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37516824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bifurcations to transient and oscillatory excitations in inhomogeneous excitable media: Insights into arrhythmogenesis in long QT syndrome.Phys Rev E. 2023 Mar;107(3-1):034402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.107.034402. Phys Rev E. 2023. PMID: 37073009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- January CT, Riddle JM, Salata JJ. A model for early afterdepolarizations: induction with the Ca2+ channel agonist Bay K 8644. Circ Res. 1988;62(3):563–71. . - PubMed
-
- Ma J, Guo L, Fiene SJ, Anson BD, Thomson JA, Kamp TJ, et al. High purity human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes: electrophysiological properties of action potentials and ionic currents. American Journal of Physiology—Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2011;301(5):H2006–H17. 10.1152/ajpheart.00694.2011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- January CT, Moscucci A. Cellular mechanisms of early afterdepolarizations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;644:23–32. . - PubMed
-
- Cranefield PF, Aronson RS. Torsade de Pointes and Other Pause-Induced Ventricular Tachycardias: The Short-Long-Short Sequence and Early Afterdepolarizations. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1988;11(6):670–8. 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1988.tb06016.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosen MR, Moak JP, Damiano B. The clinical relevance of afterdepolarizations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;427:84–93. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

