Potentiality of Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Imagery to Investigate Artificial Light Pollution
- PMID: 30200485
- PMCID: PMC6165281
- DOI: 10.3390/s18092900
Potentiality of Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Imagery to Investigate Artificial Light Pollution
Abstract
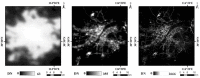
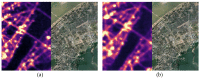
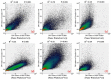
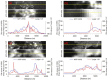
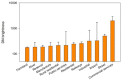
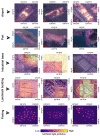
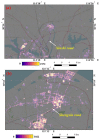
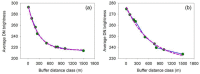
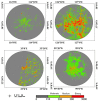
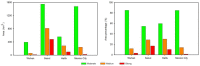
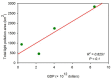
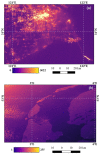
The successful launch of Luojia 1-01 complements the existing nighttime light data with a high spatial resolution of 130 m. This paper is the first study to assess the potential of using Luojia 1-01 nighttime light imagery for investigating artificial light pollution. Eight Luojia 1-01 images were selected to conduct geometric correction. Then, the ability of Luojia 1-01 to detect artificial light pollution was assessed from three aspects, including the comparison between Luojia 1-01 and the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (NPP-VIIRS), the source of artificial light pollution and the patterns of urban light pollution. Moreover, the advantages and limitations of Luojia 1-01 were discussed. The results showed the following: (1) Luojia 1-01 can detect a higher dynamic range and capture the finer spatial details of artificial nighttime light. (2) The averages of the artificial light brightness were different between various land use types. The brightness of the artificial light pollution of airports, streets, and commercial services is high, while dark areas include farmland and rivers. (3) The light pollution patterns of four cities decreased away from the urban core and the total light pollution is highly related to the economic development. Our findings confirm that Luojia 1-01 can be effectively used to investigate artificial light pollution. Some limitations of Luojia 1-01, including its spectral range, radiometric calibration and the effects of clouds and moonlight, should be researched in future studies.
Keywords: Luojia 1-01; NPP/VIIRS; human activity; light pollution; nighttime light imagery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessing the Ability of Luojia 1-01 Imagery to Detect Feeble Nighttime Lights.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Aug 26;19(17):3708. doi: 10.3390/s19173708. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31455021 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping Urban Extent Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Imagery.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Oct 29;18(11):3665. doi: 10.3390/s18113665. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30380616 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data for Mapping Global Fossil Fuel Combustion CO2 Emissions: A Comparison with DMSP-OLS Nighttime Light Data.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 21;10(9):e0138310. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138310. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26390037 Free PMC article.
-
The ecological impacts of nighttime light pollution: a mechanistic appraisal.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2013 Nov;88(4):912-27. doi: 10.1111/brv.12036. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2013. PMID: 23565807 Review.
-
In Vivo Observations of Rapid Scattered Light Changes Associated with Neurophysiological Activity.In: Frostig RD, editor. In Vivo Optical Imaging of Brain Function. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 5. In: Frostig RD, editor. In Vivo Optical Imaging of Brain Function. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 5. PMID: 26844322 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Night-light Image Restoration Method Based on Night Scattering Model for Luojia 1-01 Satellite.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Aug 30;19(17):3761. doi: 10.3390/s19173761. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31480362 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and Reduction of Solar Stray Light in the Nighttime Imaging Camera of Luojia-1 Satellite.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Mar 6;19(5):1130. doi: 10.3390/s19051130. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30845648 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Ability of Luojia 1-01 Imagery to Detect Feeble Nighttime Lights.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Aug 26;19(17):3708. doi: 10.3390/s19173708. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31455021 Free PMC article.
-
On-Orbit Signal-to-Noise Ratio Test Method for Night-Light Camera in Luojia 1-01 Satellite Based on Time-Sequence Imagery.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Sep 20;19(19):4077. doi: 10.3390/s19194077. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31547198 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Spatiotemporal Variability and Driving Factors of Artificial Lighting in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Using Remote Sensing Imagery and Socioeconomic Data.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jun 1;16(11):1950. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16111950. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31159391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mazor T., Levin N., Possingham H.P., Levy Y., Rocchini D., Richardson A.J., Kark S. Can satellite-based night lights be used for conservation? The case of nesting sea turtles in the mediterranean. Biol. Conserv. 2013;159:63–72. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2012.11.004. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

