The NFκB subunit RELA is a master transcriptional regulator of the committed epithelial-mesenchymal transition in airway epithelial cells
- PMID: 30166344
- PMCID: PMC6200927
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003662
The NFκB subunit RELA is a master transcriptional regulator of the committed epithelial-mesenchymal transition in airway epithelial cells
Abstract
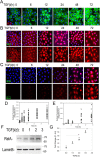
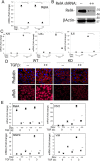
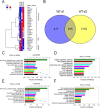
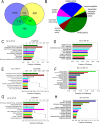
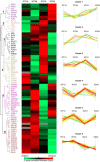
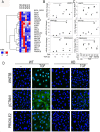
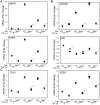
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a multistep dedifferentiation program important in tissue repair. Here, we examined the role of the transcriptional regulator NF-κB in EMT of primary human small airway epithelial cells (hSAECs). Surprisingly, transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) activated NF-κB/RELA proto-oncogene, NF-κB subunit (RELA) translocation within 1 day of stimulation, yet induction of its downstream gene regulatory network occurred only after 3 days. A time course of TGFβ-induced EMT transition was analyzed by RNA-Seq in the absence or presence of inducible shRNA-mediated silencing of RELA. In WT cells, TGFβ stimulation significantly affected the expression of 2,441 genes. Gene set enrichment analysis identified WNT, cadherin, and NF-κB signaling as the most prominent TGFβ-inducible pathways. By comparison, RELA controlled expression of 3,138 overlapping genes mapping to WNT, cadherin, and chemokine signaling pathways. Conducting upstream regulator analysis, we found that RELA controls six clusters of upstream transcription factors, many of which overlapped with a transcription factor topology map of EMT developed earlier. RELA triggered expression of three key EMT pathways: 1) the WNT/β-catenin morphogen pathway, 2) the JUN transcription factor, and 3) the Snail family transcriptional repressor 1 (SNAI1). RELA binding to target genes was confirmed by ChIP. Experiments independently validating WNT dependence on RELA were performed by silencing RELA via genome editing and indicated that TGFβ-induced WNT5B expression and downstream activation of the WNT target AXIN2 are RELA-dependent. We conclude that RELA is a master transcriptional regulator of EMT upstream of WNT morphogen, JUN, SNAI1-ZEB1, and interleukin-6 autocrine loops.
Keywords: NF-κB; RELA proto-oncogene; Wnt; ZEB; epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT); gene regulation; lung disease; mucosal injury; transcription regulation; transforming growth factor β (TGF-β).
© 2018 Tian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of the TGFβ-induced program in primary airway epithelial cells shows essential role of NF-κB/RelA signaling network in type II epithelial mesenchymal transition.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jul 18;16(1):529. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1707-x. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26187636 Free PMC article.
-
BRD4 mediates NF-κB-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis via transcriptional elongation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):L1183-L1201. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00224.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27793799 Free PMC article.
-
Osthole inhibited TGF β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by suppressing NF-κB mediated Snail activation in lung cancer A549 cells.Cell Adh Migr. 2017 Sep 3;11(5-6):464-475. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2016.1259058. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Cell Adh Migr. 2017. PMID: 28146373 Free PMC article.
-
The novel role of Yin Yang 1 in the regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer via the dysregulated NF-κB/Snail/YY1/RKIP/PTEN Circuitry.Crit Rev Oncog. 2011;16(3-4):211-26. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.v16.i3-4.50. Crit Rev Oncog. 2011. PMID: 22248055 Review.
-
Hedgehog signaling, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and miRNA (review).Int J Mol Med. 2008 Sep;22(3):271-5. Int J Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18698484 Review.
Cited by
-
NFκB-Mediated Expression of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase δ Is Critical for Mesenchymal Transition in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells.Cells. 2023 Jan 4;12(2):207. doi: 10.3390/cells12020207. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36672142 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targets for inflammation-mediated airway remodeling in chronic lung disease.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2018 Nov;12(11):931-939. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2018.1526677. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 30241450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RSV Reprograms the CDK9•BRD4 Chromatin Remodeling Complex to Couple Innate Inflammation to Airway Remodeling.Viruses. 2020 Apr 22;12(4):472. doi: 10.3390/v12040472. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32331282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copy number gain of ACTN4 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2023 Aug;114(8):3411-3422. doi: 10.1111/cas.15841. Epub 2023 May 24. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 37226638 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ACTN4 in Tumorigenesis, Metastasis, and EMT.Cells. 2019 Nov 13;8(11):1427. doi: 10.3390/cells8111427. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31766144 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

