Genome contact map explorer: a platform for the comparison, interactive visualization and analysis of genome contact maps
- PMID: 28973466
- PMCID: PMC5622372
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx644
Genome contact map explorer: a platform for the comparison, interactive visualization and analysis of genome contact maps
Abstract
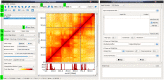
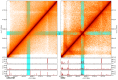
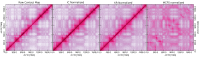
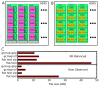
Hi-C experiments generate data in form of large genome contact maps (Hi-C maps). These show that chromosomes are arranged in a hierarchy of three-dimensional compartments. But to understand how these compartments form and by how much they affect genetic processes such as gene regulation, biologists and bioinformaticians need efficient tools to visualize and analyze Hi-C data. However, this is technically challenging because these maps are big. In this paper, we remedied this problem, partly by implementing an efficient file format and developed the genome contact map explorer platform. Apart from tools to process Hi-C data, such as normalization methods and a programmable interface, we made a graphical interface that let users browse, scroll and zoom Hi-C maps to visually search for patterns in the Hi-C data. In the software, it is also possible to browse several maps simultaneously and plot related genomic data. The software is openly accessible to the scientific community.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Using the NCBI Map Viewer to browse genomic sequence data.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2007 Jan;Chapter 1:Unit 1.5. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0105s16. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 18428781
-
3D-GNOME: an integrated web service for structural modeling of the 3D genome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 8;44(W1):W288-93. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw437. Epub 2016 May 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27185892 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization techniques for genomic data.Proc IEEE Comput Soc Bioinform Conf. 2002;1:321-6. Proc IEEE Comput Soc Bioinform Conf. 2002. PMID: 15838148 Review.
-
SeeGH--a software tool for visualization of whole genome array comparative genomic hybridization data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2004 Feb 9;5:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-13. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15040819 Free PMC article.
-
A brief introduction to web-based genome browsers.Brief Bioinform. 2013 Mar;14(2):131-43. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs029. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Brief Bioinform. 2013. PMID: 22764121 Review.
Cited by
-
3D genome mapping identifies subgroup-specific chromosome conformations and tumor-dependency genes in ependymoma.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 21;14(1):2300. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38044-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37085539 Free PMC article.
-
Cooler: scalable storage for Hi-C data and other genomically labeled arrays.Bioinformatics. 2020 Jan 1;36(1):311-316. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz540. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 31290943 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA ROR1‑AS1 high expression and its prognostic significance in liver cancer.Oncol Rep. 2020 Jan;43(1):55-74. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7398. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 31746401 Free PMC article.
-
HCMB: A stable and efficient algorithm for processing the normalization of highly sparse Hi-C contact data.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Apr 27;19:2637-2645. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.04.064. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34025950 Free PMC article.
-
Hi-C analysis: from data generation to integration.Biophys Rev. 2019 Feb;11(1):67-78. doi: 10.1007/s12551-018-0489-1. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Biophys Rev. 2019. PMID: 30570701 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

