Annual variations of monsoon and drought detected by GPS: A case study in Yunnan, China
- PMID: 28724912
- PMCID: PMC5517602
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-06095-1
Annual variations of monsoon and drought detected by GPS: A case study in Yunnan, China
Abstract
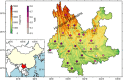
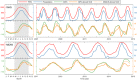
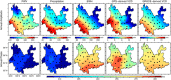
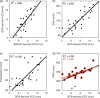
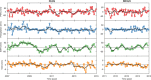
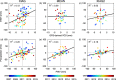
The Global Positioning System (GPS) records monsoonal precipitable water vapor (PWV) and vertical crustal displacement (VCD) due to hydrological loading, and can thus be applied jointly to diagnose meteorological and hydrological droughts. We have analyzed the PWV and VCD observations during 2007.0-2015.0 at 26 continuous GPS stations located in Yunnan province, China. We also obtained equivalent water height (EWH) derived from the Gravity Recovery And Climate Experiment (GRACE) and precipitation at these stations with the same period. Then, we quantified the annual variations of PWV, precipitation, EWH and VCD and provided empirical relationships between them. We found that GPS-derived PWV and VCD (positive means downward movement) are in phase with precipitation and GRACE-derived EWH, respectively. The annual signals of VCD and PWV show linearly correlated amplitudes and a two-month phase lag. Furthermore, the results indicate that PWV and VCD anomalies can also be used to explore drought, such as the heavy drought during winter/spring 2010. Our analysis results verify the capability of GPS to monitor monsoon variations and drought in Yunnan and show that a more comprehensive understanding of the characteristics of regional monsoon and drought can be achieved by integrating GPS-derived PWV and VCD with precipitation and GRACE-derived EWH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Space-based observations of crustal deflections for drought characterization in Brazil.Sci Total Environ. 2018 Dec 10;644:256-273. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.277. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Sci Total Environ. 2018. PMID: 29981974
-
Hydrological drought characterization based on GNSS imaging of vertical crustal deformation across the contiguous United States.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Jun 1;823:153663. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153663. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35124040
-
Potential Seasonal Terrestrial Water Storage Monitoring from GPS Vertical Displacements: A Case Study in the Lower Three-Rivers Headwater Region, China.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Sep 19;16(9):1526. doi: 10.3390/s16091526. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27657064 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal Hydrological Loading in Southern Tibet Detected by Joint Analysis of GPS and GRACE.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Dec 4;15(12):30525-38. doi: 10.3390/s151229815. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26690157 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Global Water Storage Variability from GRACE: Trends, Seasonal Cycle, Subseasonal Anomalies and Extremes.Surv Geophys. 2016;37:357-395. doi: 10.1007/s10712-016-9367-1. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Surv Geophys. 2016. PMID: 27471333 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improved Drought Monitoring Index Using GNSS-Derived Precipitable Water Vapor over the Loess Plateau Area.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Dec 16;19(24):5566. doi: 10.3390/s19245566. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31888304 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of Local Effects and Surface Loads on the Common Mode Error Filtering in Continuous GPS Measurements in the Northwest of Yunnan Province, China.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Sep 21;20(18):5408. doi: 10.3390/s20185408. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32967242 Free PMC article.
-
A web-based GPS system for displacement monitoring and failure mechanism analysis of reservoir landslide.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 7;7(1):17171. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17507-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29215051 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of GNSS/GPS in Hydrogeodesy: Hydrologic Loading Applications and Their Implications for Water Resource Research.Water Resour Res. 2022 Jul;58(7):e2022WR032078. doi: 10.1029/2022WR032078. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Water Resour Res. 2022. PMID: 36247691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large influence of soil moisture on long-term terrestrial carbon uptake.Nature. 2019 Jan;565(7740):476-479. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0848-x. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30675043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yirdaw SZ, Snelgrove KR, Agboma CO. GRACE satellite observations of terrestrial moisture changes for drought characterization in the Canadian Prairie. Journal of Hydrology. 2008;356:84–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.04.004. - DOI
-
- Chen JL, Wilson CR, Tapley BD, Yang ZL, Niu GY. 2005 drought event in the Amazon River basin as measured by GRACE and estimated by climate models. J. Geophys. Res. 2009;114:B05404.
-
- Long D, et al. GRACE satellite monitoring of large depletion in water storage in response to the 2011 drought in Texas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013;40:3395–3401. doi: 10.1002/grl.50655. - DOI
-
- Steckler MS, et al. Modeling Earth deformation from monsoonal flooding in Bangladesh using hydrographic, GPS, and Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data. J. Geophys. Res. 2010;115:B08407. doi: 10.1029/2009JB007018. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

