A Hierarchical Building Segmentation in Digital Surface Models for 3D Reconstruction
- PMID: 28125018
- PMCID: PMC5336069
- DOI: 10.3390/s17020222
A Hierarchical Building Segmentation in Digital Surface Models for 3D Reconstruction
Abstract
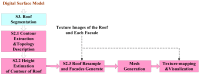
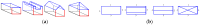
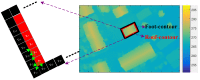
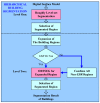
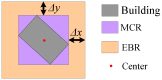
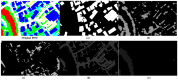
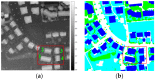
In this study, a hierarchical method for segmenting buildings in a digital surface model (DSM), which is used in a novel framework for 3D reconstruction, is proposed. Most 3D reconstructions of buildings are model-based. However, the limitations of these methods are overreliance on completeness of the offline-constructed models of buildings, and the completeness is not easily guaranteed since in modern cities buildings can be of a variety of types. Therefore, a model-free framework using high precision DSM and texture-images buildings was introduced. There are two key problems with this framework. The first one is how to accurately extract the buildings from the DSM. Most segmentation methods are limited by either the terrain factors or the difficult choice of parameter-settings. A level-set method are employed to roughly find the building regions in the DSM, and then a recently proposed 'occlusions of random textures model' are used to enhance the local segmentation of the buildings. The second problem is how to generate the facades of buildings. Synergizing with the corresponding texture-images, we propose a roof-contour guided interpolation of building facades. The 3D reconstruction results achieved by airborne-like images and satellites are compared. Experiments show that the segmentation method has good performance, and 3D reconstruction is easily performed by our framework, and better visualization results can be obtained by airborne-like images, which can be further replaced by UAV images.
Keywords: 3D reconstruction; building segmentation; digital surface model; remote sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A Dynamic Multi-Projection-Contour Approximating Framework for the 3D Reconstruction of Buildings by Super-Generalized Optical Stereo-Pairs.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Sep 19;17(9):2153. doi: 10.3390/s17092153. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28925947 Free PMC article.
-
Coherent Markov Random Field-Based Unreliable DSM Areas Segmentation and Hierarchical Adaptive Surface Fitting for InSAR DEM Reconstruction.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Mar 4;20(5):1414. doi: 10.3390/s20051414. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32143515 Free PMC article.
-
High-Rise Building 3D Reconstruction with the Wrapped Interferometric Phase.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Mar 23;19(6):1439. doi: 10.3390/s19061439. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30909595 Free PMC article.
-
Fast Building Instance Proxy Reconstruction for Large Urban Scenes.IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2024 Nov;46(11):7267-7282. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3388371. Epub 2024 Oct 3. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2024. PMID: 38625775
-
Automatic Segmentation of Multiple Organs on 3D CT Images by Using Deep Learning Approaches.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1213:135-147. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-33128-3_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32030668 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of DSMs Using Backpack-Mounted Systems and Drone Techniques to Characterise Ancient Underground Cellars in the Duero Basin (Spain).Sensors (Basel). 2019 Dec 4;19(24):5352. doi: 10.3390/s19245352. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31817242 Free PMC article.
-
Building Extraction Based on an Optimized Stacked Sparse Autoencoder of Structure and Training Samples Using LIDAR DSM and Optical Images.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Aug 24;17(9):1957. doi: 10.3390/s17091957. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28837118 Free PMC article.
-
Roof Shape Classification from LiDAR and Satellite Image Data Fusion Using Supervised Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Nov 15;18(11):3960. doi: 10.3390/s18113960. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30445731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin L., Zhu L., Gong H., Pan Y., Du L. Design and development of wetland evaluation system based on remote sensing and 3D visualization; Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling; Taiyuan, China. 22–24 October 2010; pp. 170–173.
-
- Zhang L., Han C., Zhang L., Zhang X., Li J. Web-based visualization of large 3D urban building models. Int. J. Digit. Earth. 2014;7:53–67. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2012.667159. - DOI
-
- Saito K., Spence R. Mapping urban building stocks for vulnerability assessment—Preliminary results. Int. J. Digit. Earth. 2011;4:117–130. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2010.513114. - DOI
-
- Cheng L., Gong J., Li M., Liu Y. 3D building model reconstruction from multi-view aerial imagery and LIDAR data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2011;77:125–139. doi: 10.14358/PERS.77.2.125. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

