Two-UAV Intersection Localization System Based on the Airborne Optoelectronic Platform
- PMID: 28067814
- PMCID: PMC5298671
- DOI: 10.3390/s17010098
Two-UAV Intersection Localization System Based on the Airborne Optoelectronic Platform
Abstract
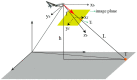
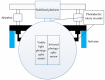
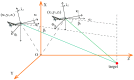
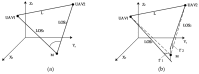
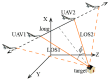
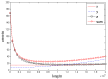
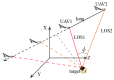
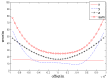
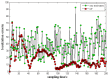
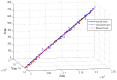
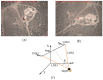
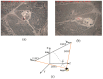
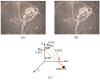
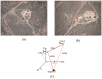
To address the limitation of the existing UAV (unmanned aerial vehicles) photoelectric localization method used for moving objects, this paper proposes an improved two-UAV intersection localization system based on airborne optoelectronic platforms by using the crossed-angle localization method of photoelectric theodolites for reference. This paper introduces the makeup and operating principle of intersection localization system, creates auxiliary coordinate systems, transforms the LOS (line of sight, from the UAV to the target) vectors into homogeneous coordinates, and establishes a two-UAV intersection localization model. In this paper, the influence of the positional relationship between UAVs and the target on localization accuracy has been studied in detail to obtain an ideal measuring position and the optimal localization position where the optimal intersection angle is 72.6318°. The result shows that, given the optimal position, the localization root mean square error (RMS) will be 25.0235 m when the target is 5 km away from UAV baselines. Finally, the influence of modified adaptive Kalman filtering on localization results is analyzed, and an appropriate filtering model is established to reduce the localization RMS error to 15.7983 m. Finally, An outfield experiment was carried out and obtained the optimal results: σ B = 1.63 × 10 - 4 ( ° ) , σ L = 1.35 × 10 - 4 ( ° ) , σ H = 15.8 ( m ) , σ s u m = 27.6 ( m ) , where σ B represents the longitude error, σ L represents the latitude error, σ H represents the altitude error, and σ s u m represents the error radius.
Keywords: UAV (unmanned aerial vehicles); accuracy analysis; adaptive Kalman filtering; airborne optoelectronic platform; coordinate transformation; intersection localization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
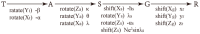
Similar articles
-
Real-Time Multi-Target Localization from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Dec 25;17(1):33. doi: 10.3390/s17010033. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28029145 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel System for Correction of Relative Angular Displacement between Airborne Platform and UAV in Target Localization.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Mar 4;17(3):510. doi: 10.3390/s17030510. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28273845 Free PMC article.
-
An Augmented Reality Geo-Registration Method for Ground Target Localization from a Low-Cost UAV Platform.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Nov 2;18(11):3739. doi: 10.3390/s18113739. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30400206 Free PMC article.
-
The Recent Advancement in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Tracking Antenna: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Aug 23;21(16):5662. doi: 10.3390/s21165662. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A meta-analysis of human-system interfaces in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) swarm management.Appl Ergon. 2017 Jan;58:66-80. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2016.05.011. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Appl Ergon. 2017. PMID: 27633199 Review.
Cited by
-
Precise Target Geo-Location of Long-Range Oblique Reconnaissance System for UAVs.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Feb 28;22(5):1903. doi: 10.3390/s22051903. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35271049 Free PMC article.
-
Signal Source Localization with Long-Term Observations in Distributed Angle-Only Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 9;22(24):9655. doi: 10.3390/s22249655. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560025 Free PMC article.
-
High-Accuracy Calibration Based on Linearity Adjustment for Eddy Current Displacement Sensor.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Aug 28;18(9):2842. doi: 10.3390/s18092842. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30154354 Free PMC article.
-
RF-Based UAV Detection and Identification Using Hierarchical Learning Approach.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 10;21(6):1947. doi: 10.3390/s21061947. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802189 Free PMC article.
-
An Improved Unauthorized Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Detection Algorithm Using Radiofrequency-Based Statistical Fingerprint Analysis.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jan 11;19(2):274. doi: 10.3390/s19020274. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30641959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eric J.S. Geo-Pointing and Threat Location Techniques for Airborne Border Surveillance; Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Technologies for Homeland Security (HST); Waltham, MA, USA. 12–14 November 2013; pp. 136–140.
-
- Gao F., Ma X., Gu J., Li Y. An Active Target Localization with Moncular Vision; Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Control & Automation (ICCA); Taichung, Taiwan. 18–21 June 2014; pp. 1381–1386.
-
- Su L., Hao Q. Study on Intersection Measurement and Error Analysis; Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling (ICCASM); Taiyuan, China. 22–24 October 2010.
-
- Liu L., Liu L. Intersection Measuring System of Trajectory Camera with Long Narrow Photosensitive Surface; Proceedings of the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE); Beijing, China. 26 January 2006; pp. 1006–1011.
-
- Hu T. Double UAV Cooperative Localization and Remote Location Error Analysis; Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering; Shenzhen, China. 19–20 September 2015; pp. 76–81.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

