A Context-Recognition-Aided PDR Localization Method Based on the Hidden Markov Model
- PMID: 27916922
- PMCID: PMC5191011
- DOI: 10.3390/s16122030
A Context-Recognition-Aided PDR Localization Method Based on the Hidden Markov Model
Abstract
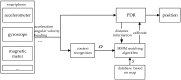
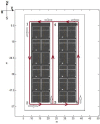
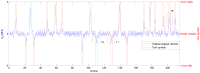
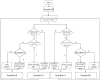
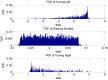
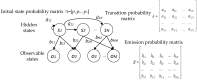
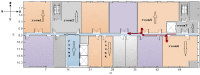
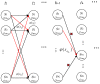
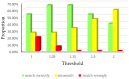
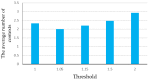
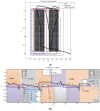
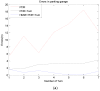
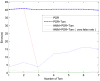
Indoor positioning has recently become an important field of interest because global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are usually unavailable in indoor environments. Pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR) is a promising localization technique for indoor environments since it can be implemented on widely used smartphones equipped with low cost inertial sensors. However, the PDR localization severely suffers from the accumulation of positioning errors, and other external calibration sources should be used. In this paper, a context-recognition-aided PDR localization model is proposed to calibrate PDR. The context is detected by employing particular human actions or characteristic objects and it is matched to the context pre-stored offline in the database to get the pedestrian's location. The Hidden Markov Model (HMM) and Recursive Viterbi Algorithm are used to do the matching, which reduces the time complexity and saves the storage. In addition, the authors design the turn detection algorithm and take the context of corner as an example to illustrate and verify the proposed model. The experimental results show that the proposed localization method can fix the pedestrian's starting point quickly and improves the positioning accuracy of PDR by 40.56% at most with perfect stability and robustness at the same time.
Keywords: HMM; PDR; context recognition; indoor localization; turn detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Smartphone-Based 3D Indoor Pedestrian Positioning through Multi-Modal Data Fusion.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Oct 19;19(20):4554. doi: 10.3390/s19204554. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31635127 Free PMC article.
-
The Performance Analysis of the Map-Aided Fuzzy Decision Tree Based on the Pedestrian Dead Reckoning Algorithm in an Indoor Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Dec 28;16(1):34. doi: 10.3390/s16010034. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26729114 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Smartphone MEMS Sensors and Environmental Prior Information for Pedestrian Indoor Positioning.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Apr 16;20(8):2263. doi: 10.3390/s20082263. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32316230 Free PMC article.
-
Use of high sensitivity GNSS receiver Doppler measurements for indoor pedestrian dead reckoning.Sensors (Basel). 2013 Mar 28;13(4):4303-26. doi: 10.3390/s130404303. Sensors (Basel). 2013. PMID: 23539033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Pedestrian Indoor Positioning Systems for Mass Market Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Aug 22;17(8):1927. doi: 10.3390/s17081927. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28829386 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep Learning-Based Positioning of Visually Impaired People in Indoor Environments.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Oct 31;20(21):6238. doi: 10.3390/s20216238. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33142927 Free PMC article.
-
Research on PF-SLAM Indoor Pedestrian Localization Algorithm Based on Feature Point Map.Micromachines (Basel). 2018 May 28;9(6):267. doi: 10.3390/mi9060267. Micromachines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30424200 Free PMC article.
-
Geomagnetism-Aided Indoor Wi-Fi Radio-Map Construction via Smartphone Crowdsourcing.Sensors (Basel). 2018 May 8;18(5):1462. doi: 10.3390/s18051462. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29738454 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility Analysis of Magnetic Navigation for Vehicles.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Dec 9;19(24):5410. doi: 10.3390/s19245410. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31818041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu W. Master’s Thesis. Central China Normal University; Wuhan, China: 2014. Research and Implementation of Indoor Positioning Based on the Android Mobile Phone.
-
- Li W., Wei D.Y., Yuan H., Ouyang G.Z. A novel method of WiFi fingerprint positioning using spatial multi-points matching; Proceedings of the International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN); Alcalá de Henares, Spain. 4–5 October 2016.
-
- Huang C.M., Hsieh T.H., Lin S.Y. A signal-aware fingerprinting-based positioning technique in cellular networks; Proceedings of the 2011 14th International Conference on Network-Based Information Systems (NBiS); Tirana, Albania. 7–9 September 2011; pp. 325–332.
-
- Yao T.J., Wei D.Y., Yuan H. Research on the feedback correction-based fusion method for WLAN and PDR positioning. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2016;37:446–453.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

