Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: What Polyphenols Can Do for Us?
- PMID: 27738491
- PMCID: PMC5055983
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/7432797
Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: What Polyphenols Can Do for Us?
Abstract
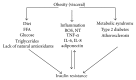
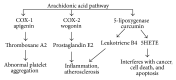
Oxidative stress is viewed as an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and their elimination by protective mechanisms, which can lead to chronic inflammation. Oxidative stress can activate a variety of transcription factors, which lead to the differential expression of some genes involved in inflammatory pathways. The inflammation triggered by oxidative stress is the cause of many chronic diseases. Polyphenols have been proposed to be useful as adjuvant therapy for their potential anti-inflammatory effect, associated with antioxidant activity, and inhibition of enzymes involved in the production of eicosanoids. This review aims at exploring the properties of polyphenols in anti-inflammation and oxidation and the mechanisms of polyphenols inhibiting molecular signaling pathways which are activated by oxidative stress, as well as the possible roles of polyphenols in inflammation-mediated chronic disorders. Such data can be helpful for the development of future antioxidant therapeutics and new anti-inflammatory drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;129:110452. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110452. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32768946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Chlorogenic Acids in Controlling Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress Conditions.Nutrients. 2015 Dec 25;8(1):16. doi: 10.3390/nu8010016. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 26712785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial Cells: From Dysfunction Mechanism to Pharmacological Effect in Cardiovascular Disease.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2019 Feb;19(1):13-22. doi: 10.1007/s12012-018-9493-8. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30506414 Review.
-
The effects of polyphenols on oxidative stress and the arachidonic acid cascade. Implications for the prevention/treatment of high prevalence diseases.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Nov 1;84(9):1113-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.07.017. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22858365
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of anthocyanins via modulation of nuclear factor-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades.Nutr Rev. 2015 Jun;73(6):348-58. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuu066. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Nutr Rev. 2015. PMID: 26011910 Review.
Cited by
-
Polyphenols Regulate the Activity of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals, Having Both Positive and Negative Effects.J Xenobiot. 2024 Oct 2;14(4):1378-1405. doi: 10.3390/jox14040077. J Xenobiot. 2024. PMID: 39449418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Polyphenols in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Oct 14;20(14):5608-5672. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.98107. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39494333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Fortification with Raspberry Juice on the Antioxidant and Potentially Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Wafers Subjected to In Vitro Digestion.Foods. 2021 Apr 7;10(4):791. doi: 10.3390/foods10040791. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33916956 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Strategies on Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress: A Narrative Review of Human Studies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 31;10(4):542. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040542. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chestnut Shell Tannins: Effects on Intestinal Inflammation and Dysbiosis in Zebrafish.Animals (Basel). 2021 May 25;11(6):1538. doi: 10.3390/ani11061538. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34070355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ďuračková Z. Some current insights into oxidative stress. Physiological Research. 2010;59(4):459–469. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S., Pandey A. K. Free radicals: health implications and their mitigation by herbals. British Journal of Medicine and Medical Research. 2015;7(6):438–457. doi: 10.9734/bjmmr/2015/16284. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical