Automatic Authorship Detection Using Textual Patterns Extracted from Integrated Syntactic Graphs
- PMID: 27589740
- PMCID: PMC5038652
- DOI: 10.3390/s16091374
Automatic Authorship Detection Using Textual Patterns Extracted from Integrated Syntactic Graphs
Abstract
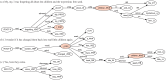
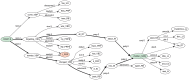
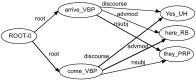
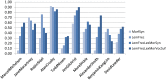
We apply the integrated syntactic graph feature extraction methodology to the task of automatic authorship detection. This graph-based representation allows integrating different levels of language description into a single structure. We extract textual patterns based on features obtained from shortest path walks over integrated syntactic graphs and apply them to determine the authors of documents. On average, our method outperforms the state of the art approaches and gives consistently high results across different corpora, unlike existing methods. Our results show that our textual patterns are useful for the task of authorship attribution.
Keywords: authorship attribution; authorship verification; integrated syntactic graphs; shortest paths walks; syntactic n-grams; textual patterns.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Path-based knowledge reasoning with textual semantic information for medical knowledge graph completion.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021 Nov 29;21(Suppl 9):335. doi: 10.1186/s12911-021-01622-7. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021. PMID: 34844576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Authorship attribution based on Life-Like Network Automata.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 22;13(3):e0193703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193703. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29566100 Free PMC article.
-
Learning Stylometric Representations for Authorship Analysis.IEEE Trans Cybern. 2019 Jan;49(1):107-121. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2766189. Epub 2017 Nov 21. IEEE Trans Cybern. 2019. PMID: 29990260
-
Multi-way association extraction and visualization from biological text documents using hyper-graphs: applications to genetic association studies for diseases.Artif Intell Med. 2010 Jul;49(3):145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2010.03.002. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Artif Intell Med. 2010. PMID: 20382004
-
Authorship identification of documents with high content similarity.Scientometrics. 2018;115(1):223-237. doi: 10.1007/s11192-018-2661-6. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Scientometrics. 2018. PMID: 29527072 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Deep neural network and model-based clustering technique for forensic electronic mail author attribution.SN Appl Sci. 2021;3(3):348. doi: 10.1007/s42452-020-04127-6. Epub 2021 Feb 18. SN Appl Sci. 2021. PMID: 33619463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mihalcea R., Radev D. Graph-Based Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval. MIT Press; Cambridge, NY, USA: 2011.
-
- Pinto D., Gómez-Adorno H., Vilariño D., Singh V.K. A graph-based multi-level linguistic representation for document understanding. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014;41:93–102. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2013.12.004. - DOI
-
- Sidorov G., Velasquez F., Stamatatos E., Gelbukh A., Chanona-Hernández L. Syntactic N-grams as machine learning features for natural language processing. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013;41:853–860. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2013.08.015. - DOI
-
- Salton G., editor. Automatic Text Processing. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc.; Boston, MA, USA: 1988.
-
- Ruiz Costa-jussà M. Segmentation strategies to face morphology challenges in Brazilian-Portuguese/English statistical machine translation and its integration in cross-language information retrieval. Comput. Sist. 2015;19:357–370. doi: 10.13053/cys-19-2-1550. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

