Assessing the Contribution of the Environmental Parameters to Eutrophication with the Use of the "PaD" and "PaD2" Methods in a Hypereutrophic Lake
- PMID: 27483293
- PMCID: PMC4997450
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph13080764
Assessing the Contribution of the Environmental Parameters to Eutrophication with the Use of the "PaD" and "PaD2" Methods in a Hypereutrophic Lake
Abstract
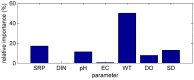
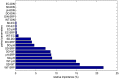
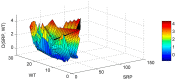
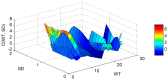
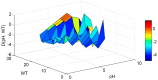
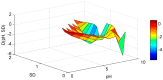
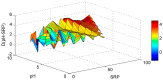
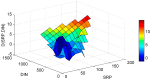
Lake Pamvotis (Greece) is a shallow hypereutrophic lake with a natural tendency to eutrophication. Several restoration measures were applied, but with no long-term success. To examine the causes for this an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) was created in order to simulate the chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) levels and to investigate the role of the associated environmental parameters. The ANN managed to simulate with good correlation the simulated Chl-a and can be considered as a reliable predictor. The relative importance of the environmental parameters to the simulated Chl-a was calculated with the use of the "Partial Derivatives" ("PaD") sensitivity method. The water temperature (WT) and soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP) had the highest relative importance, with values of 50% and 17%, respectively. The synergistic effect of the paired parameters was calculated with the use of the "PaD2" algorithm. The SRP-WT paired parameter was the most influential, with a relative contribution of 22%. The ANN showed that Lake Pamvotis is prone to suffer the effects of climatic change, because of the major contribution of WT. The ANN also revealed that combined nutrients reduction would improve water quality status. The ANN findings can act as an advisory tool regarding any restoration efforts.
Keywords: Artificial Neural Network; environmental parameter; eutrophication; lake; “PaD2” method; “PaD” method.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long term changes in the eutrophication process in a shallow Mediterranean lake ecosystem of W. Greece: response after the reduction of external load.J Environ Manage. 2008 May;87(3):497-506. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.01.039. Epub 2007 Mar 26. J Environ Manage. 2008. PMID: 17383796
-
Integration of Bayesian analysis for eutrophication prediction and assessment in a landscape lake.Environ Monit Assess. 2015 Jan;187(1):4169. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-4169-8. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Environ Monit Assess. 2015. PMID: 25467413
-
A three-dimensional water quality modeling approach for exploring the eutrophication responses to load reduction scenarios in Lake Yilong (China).Environ Pollut. 2013 Jun;177:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.01.047. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Environ Pollut. 2013. PMID: 23455397
-
Modelling eutrophication in lake ecosystems: A review.Sci Total Environ. 2019 Feb 15;651(Pt 2):2985-3001. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.320. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 30463149 Review.
-
Indices and models of surface water quality assessment: Review and perspectives.Environ Pollut. 2022 Sep 1;308:119611. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119611. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Environ Pollut. 2022. PMID: 35716892 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the Eutrophication-Related Environmental Parameters in Two Mediterranean Lakes by Integrating Statistical Techniques and Self-Organizing Maps.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Mar 19;15(3):547. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15030547. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29562675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dyhrman S.T. Molecular approaches to diagnosing nutritional physiology in harmful algae: Implications for studying the effects of eutrophication. Harmful Algae. 2008;8:167–174. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2008.08.016. - DOI
-
- Ferreira J.G., Andersen J.H., Borja A., Bricker S.B., Camp J., Cardoso da Silva M., Garcés E., Heiskanen A.S., Humborg C., Ignatiades L., et al. Overview of eutrophication indicators to assess environmental status within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011;93:117–131. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.03.014. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

