Predicting the three-dimensional folding of cis-regulatory regions in mammalian genomes using bioinformatic data and polymer models
- PMID: 27036497
- PMCID: PMC4815170
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-016-0909-0
Predicting the three-dimensional folding of cis-regulatory regions in mammalian genomes using bioinformatic data and polymer models
Abstract
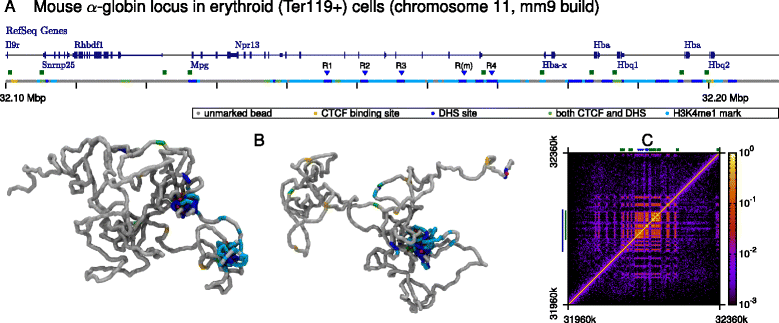
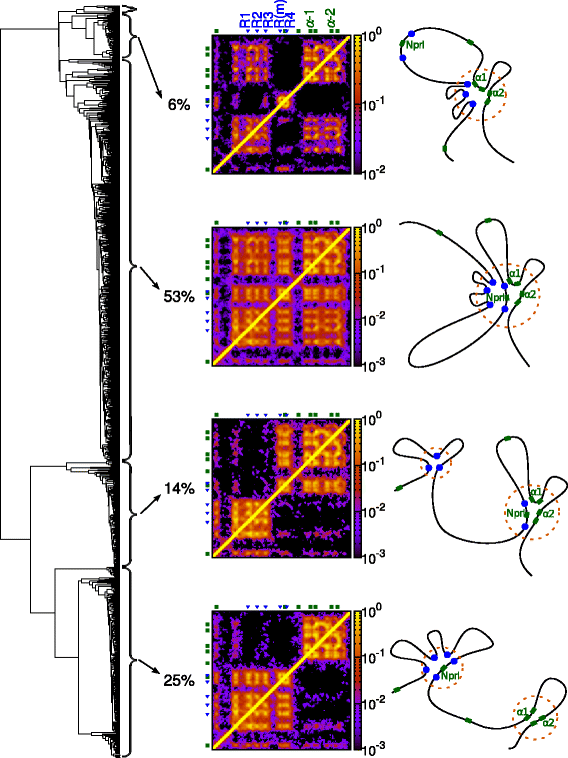
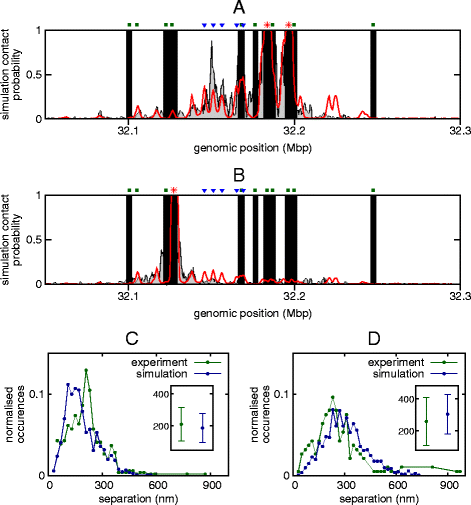
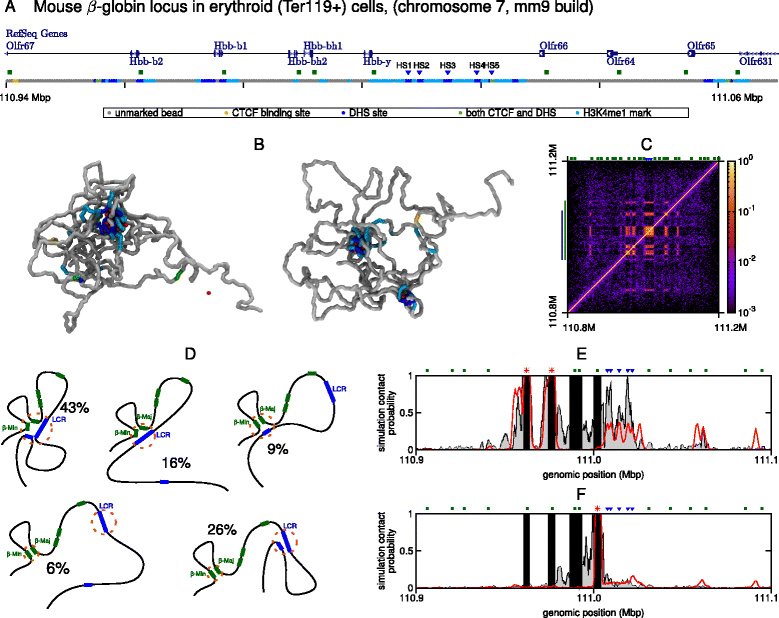
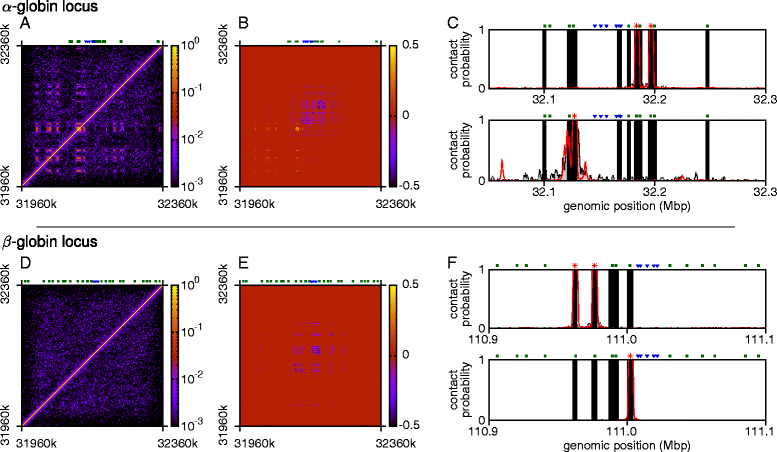
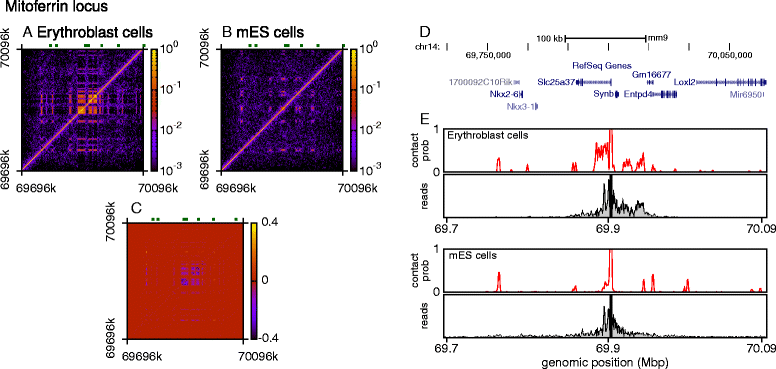
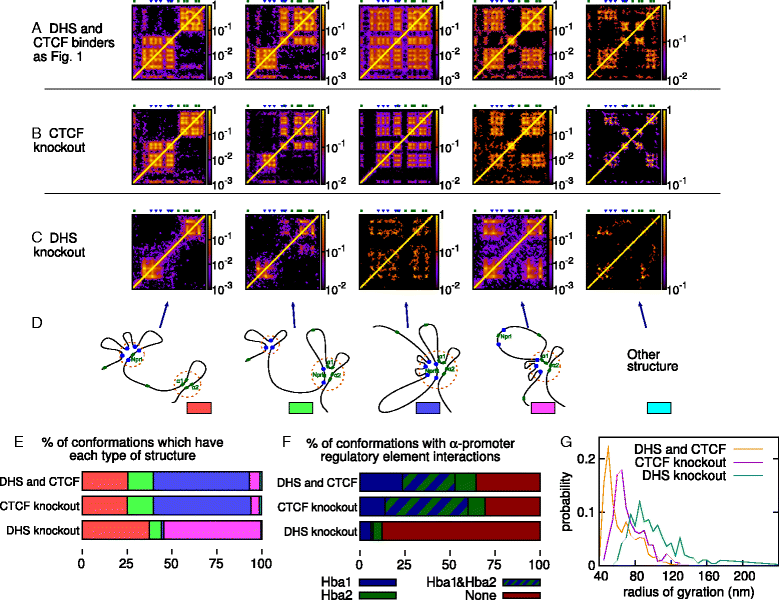
The three-dimensional (3D) organization of chromosomes can be probed using methods like Capture-C. However, it is unclear how such population-level data relate to the organization within a single cell, and the mechanisms leading to the observed interactions are still largely obscure. We present a polymer modeling scheme based on the assumption that chromosome architecture is maintained by protein bridges, which form chromatin loops. To test the model, we perform FISH experiments and compare with Capture-C data. Starting merely from the locations of protein binding sites, our model accurately predicts the experimentally observed chromatin interactions, revealing a population of 3D conformations.
Keywords: Chromosome conformation; Fluorescence in situ hybridization; Polymer model; cis-regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polymer Simulations of Heteromorphic Chromatin Predict the 3D Folding of Complex Genomic Loci.Mol Cell. 2018 Nov 15;72(4):786-797.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.09.016. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30344096 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation of different three-dimensional polymer models of interphase chromosomes compared to experiments-an evaluation and review framework of the 3D genome organization.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Jun;90:19-42. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.07.012. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30125668 Review.
-
Heterogeneous Loop Model to Infer 3D Chromosome Structures from Hi-C.Biophys J. 2019 Aug 6;117(3):613-625. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.06.032. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Biophys J. 2019. PMID: 31337548 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Hi-C and FISH data for modeling of the 3D organization of chromosomes.Nat Commun. 2019 May 3;10(1):2049. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10005-6. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31053705 Free PMC article.
-
Computational approaches from polymer physics to investigate chromatin folding.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020 Jun;64:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.01.002. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32045823 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review of computational prediction of genome-wide features.Brief Bioinform. 2020 Jan 17;21(1):120-134. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby110. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 30462144 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous interactions and polymer entropy decide organization and dynamics of chromatin domains.Biophys J. 2022 Jul 19;121(14):2794-2812. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.06.008. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 35672951 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic modeling of chromatin folding to understand function.Nat Methods. 2020 Aug;17(8):767-775. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-0852-6. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Nat Methods. 2020. PMID: 32514111 Review.
-
Predictive Polymer Models for 3D Chromosome Organization.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2301:267-291. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1390-0_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34415541 Review.
-
Extrusion without a motor: a new take on the loop extrusion model of genome organization.Nucleus. 2018 Jan 1;9(1):95-103. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2017.1421825. Nucleus. 2018. PMID: 29300120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lieberman-Aiden E, van Berkum NL, Williams L, Imakaev M, Ragoczy T, Telling A, Amit I, Lajoie BR, Sabo PJ, Dorschner MO, Sandstrom R, Bernstein B, Bender MA, Groudine M, Gnirke A, Stamatoyannopoulos J, Mirny LA, Lander ES, Dekker J. Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science. 2009;326:289–93. doi: 10.1126/science.1181369. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rao SSP, Huntley MH, Durand NC, Stamenova EK, Bochkov ID, Robinson JT, Sanborn AL, Machol I, Omer AD, Lander ES, Lieberman-Aiden E. A 3D map of the human genome at kilobase resolution reveals principles of chromatin looping. Cell. 2014;159:1665–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

