Systematic discovery of Xist RNA binding proteins
- PMID: 25843628
- PMCID: PMC4425988
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.025
Systematic discovery of Xist RNA binding proteins
Abstract
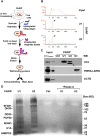
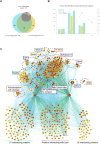
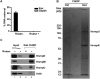
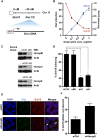
Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) function with associated proteins to effect complex structural and regulatory outcomes. To reveal the composition and dynamics of specific noncoding RNA-protein complexes (RNPs) in vivo, we developed comprehensive identification of RNA binding proteins by mass spectrometry (ChIRP-MS). ChIRP-MS analysis of four ncRNAs captures key protein interactors, including a U1-specific link to the 3' RNA processing machinery. Xist, an essential lncRNA for X chromosome inactivation (XCI), interacts with 81 proteins from chromatin modification, nuclear matrix, and RNA remodeling pathways. The Xist RNA-protein particle assembles in two steps coupled with the transition from pluripotency to differentiation. Specific interactors include HnrnpK, which participates in Xist-mediated gene silencing and histone modifications but not Xist localization, and Drosophila Split ends homolog Spen, which interacts via the A-repeat domain of Xist and is required for gene silencing. Thus, Xist lncRNA engages with proteins in a modular and developmentally controlled manner to coordinate chromatin spreading and silencing.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spen links RNA-mediated endogenous retrovirus silencing and X chromosome inactivation.Elife. 2020 May 7;9:e54508. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54508. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32379046 Free PMC article.
-
The Xist lncRNA interacts directly with SHARP to silence transcription through HDAC3.Nature. 2015 May 14;521(7551):232-6. doi: 10.1038/nature14443. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25915022 Free PMC article.
-
SPEN integrates transcriptional and epigenetic control of X-inactivation.Nature. 2020 Feb;578(7795):455-460. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1974-9. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32025035 Free PMC article.
-
Progress toward understanding chromosome silencing by Xist RNA.Genes Dev. 2020 Jun 1;34(11-12):733-744. doi: 10.1101/gad.337196.120. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32482714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA binding proteins implicated in Xist-mediated chromosome silencing.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Aug;56:58-70. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.01.029. Epub 2016 Jan 24. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26816113 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory non-coding RNAs: everything is possible, but what is important?Nat Methods. 2022 Oct;19(10):1156-1159. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01629-6. Nat Methods. 2022. PMID: 36203023 No abstract available.
-
The landscape of epigenetic regulation and therapeutic application of N6-methyladenosine modifications in non-coding RNAs.Genes Dis. 2023 Jul 18;11(5):101045. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.06.015. eCollection 2024 Sep. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 38988321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of RUF6 ncRNA-interacting proteins involved in P. falciparum immune evasion.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Nov 15;6(1):e202201577. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201577. Print 2023 Jan. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 36379669 Free PMC article.
-
Grabbing the genome by the NADs.Chromosoma. 2016 Jun;125(3):361-71. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0527-8. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Chromosoma. 2016. PMID: 26174338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA XIST regulates breast cancer stem cells by activating proinflammatory IL-6/STAT3 signaling.Oncogene. 2023 May;42(18):1419-1437. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02652-3. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36922677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown CJ, Willard HF. The human X-inactivation centre is not required for maintenance of X-chromosome inactivation. Nature. 1994;368:154–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

