Searching for superspreaders of information in real-world social media
- PMID: 24989148
- PMCID: PMC4080224
- DOI: 10.1038/srep05547
Searching for superspreaders of information in real-world social media
Abstract
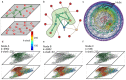
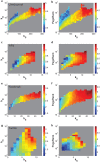
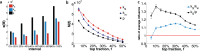
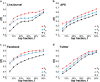
A number of predictors have been suggested to detect the most influential spreaders of information in online social media across various domains such as Twitter or Facebook. In particular, degree, PageRank, k-core and other centralities have been adopted to rank the spreading capability of users in information dissemination media. So far, validation of the proposed predictors has been done by simulating the spreading dynamics rather than following real information flow in social networks. Consequently, only model-dependent contradictory results have been achieved so far for the best predictor. Here, we address this issue directly. We search for influential spreaders by following the real spreading dynamics in a wide range of networks. We find that the widely-used degree and PageRank fail in ranking users' influence. We find that the best spreaders are consistently located in the k-core across dissimilar social platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, Livejournal and scientific publishing in the American Physical Society. Furthermore, when the complete global network structure is unavailable, we find that the sum of the nearest neighbors' degree is a reliable local proxy for user's influence. Our analysis provides practical instructions for optimal design of strategies for "viral" information dissemination in relevant applications.
Figures
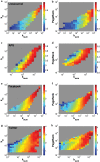
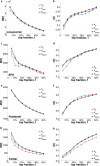
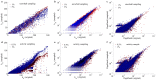
Similar articles
-
Collective Influence of Multiple Spreaders Evaluated by Tracing Real Information Flow in Large-Scale Social Networks.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 26;6:36043. doi: 10.1038/srep36043. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27782207 Free PMC article.
-
Finding Influential Spreaders from Human Activity beyond Network Location.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 31;10(8):e0136831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136831. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26323015 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting the influence of spreading in social networks with excitable sensor networks.PLoS One. 2015 May 7;10(5):e0124848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124848. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25950181 Free PMC article.
-
Algorithm-mediated social learning in online social networks.Trends Cogn Sci. 2023 Oct;27(10):947-960. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2023.06.008. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Trends Cogn Sci. 2023. PMID: 37543440 Review.
-
Social media in academics and research: 21st-century tools to turbocharge education, collaboration, and dissemination of research findings.Histopathology. 2020 Nov;77(5):688-699. doi: 10.1111/his.14196. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Histopathology. 2020. PMID: 32592211 Review.
Cited by
-
Local-Forest Method for Superspreaders Identification in Online Social Networks.Entropy (Basel). 2022 Sep 11;24(9):1279. doi: 10.3390/e24091279. Entropy (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36141165 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of strong attractors in social media networks.Comput Soc Netw. 2016;3(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40649-016-0036-9. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Comput Soc Netw. 2016. PMID: 29355206 Free PMC article.
-
Ability paradox of cascading model based on betweenness.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 10;5:13939. doi: 10.1038/srep13939. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26353903 Free PMC article.
-
Super-Spreader Identification Using Meta-Centrality.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 23;6:38994. doi: 10.1038/srep38994. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 28008949 Free PMC article.
-
Effective information spreading based on local information in correlated networks.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 2;6:38220. doi: 10.1038/srep38220. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27910882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rogers E. M. Diffusion of Innovation (Free Press, New York, 1995).
-
- Watts D. J. & Peretti J. Viral marketing for the real world. Harvard Business Review 104–112 (May2007).
-
- Gruhl D., Liben-Nowell D., Guha R. V. & Tomkins A. Information diffusion through blogspace. Proc. 13th Intl. WWW Conf. 491–501 (2004).
-
- Muchnik L., Aral S. & Taylor S. J. Social Influence Bias: A Randomized Experiment. Science 341, 647–651 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

