Improved method for linear B-cell epitope prediction using antigen's primary sequence
- PMID: 23667458
- PMCID: PMC3646881
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062216
Improved method for linear B-cell epitope prediction using antigen's primary sequence
Abstract
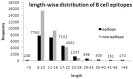
One of the major challenges in designing a peptide-based vaccine is the identification of antigenic regions in an antigen that can stimulate B-cell's response, also called B-cell epitopes. In the past, several methods have been developed for the prediction of conformational and linear (or continuous) B-cell epitopes. However, the existing methods for predicting linear B-cell epitopes are far from perfection. In this study, an attempt has been made to develop an improved method for predicting linear B-cell epitopes. We have retrieved experimentally validated B-cell epitopes as well as non B-cell epitopes from Immune Epitope Database and derived two types of datasets called Lbtope_Variable and Lbtope_Fixed length datasets. The Lbtope_Variable dataset contains 14876 B-cell epitope and 23321 non-epitopes of variable length where as Lbtope_Fixed length dataset contains 12063 B-cell epitopes and 20589 non-epitopes of fixed length. We also evaluated the performance of models on above datasets after removing highly identical peptides from the datasets. In addition, we have derived third dataset Lbtope_Confirm having 1042 epitopes and 1795 non-epitopes where each epitope or non-epitope has been experimentally validated in at least two studies. A number of models have been developed to discriminate epitopes and non-epitopes using different machine-learning techniques like Support Vector Machine, and K-Nearest Neighbor. We achieved accuracy from ∼54% to 86% using diverse s features like binary profile, dipeptide composition, AAP (amino acid pair) profile. In this study, for the first time experimentally validated non B-cell epitopes have been used for developing method for predicting linear B-cell epitopes. In previous studies, random peptides have been used as non B-cell epitopes. In order to provide service to scientific community, a web server LBtope has been developed for predicting and designing B-cell epitopes (http://crdd.osdd.net/raghava/lbtope/).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Linear B-Cell Epitope Prediction for In Silico Vaccine Design: A Performance Review of Methods Available via Command-Line Interface.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 22;22(6):3210. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063210. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33809918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of B-cell epitopes in an antigen for inducing specific class of antibodies.Biol Direct. 2013 Oct 30;8:27. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-8-27. Biol Direct. 2013. PMID: 24168386 Free PMC article.
-
EPMLR: sequence-based linear B-cell epitope prediction method using multiple linear regression.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Dec 19;15(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12859-014-0414-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 25523327 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of linear B-cell epitopes of hepatitis C virus for vaccine development.BMC Med Genomics. 2015;8 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S3. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-8-S4-S3. Epub 2015 Dec 9. BMC Med Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26680271 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-perspectives and challenges in identifying B-cell epitopes.Protein Sci. 2023 Nov;32(11):e4785. doi: 10.1002/pro.4785. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37733481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ZikaVR: An Integrated Zika Virus Resource for Genomics, Proteomics, Phylogenetic and Therapeutic Analysis.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 16;6:32713. doi: 10.1038/srep32713. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27633273 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the predictive ability of computational epitope prediction methods on Fel d 1 and other allergens.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 23;19(8):e0306254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306254. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39178274 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in antibody discovery from human BCR repertoires.Front Bioinform. 2022 Oct 20;2:1044975. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2022.1044975. eCollection 2022. Front Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36338807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linear B-Cell Epitope Prediction for In Silico Vaccine Design: A Performance Review of Methods Available via Command-Line Interface.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 22;22(6):3210. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063210. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33809918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Silico Identification of Novel Immunogenic Secreted Proteins of Mycoplasma bovis from Secretome Data and Experimental Verification.Pathogens. 2020 Sep 21;9(9):770. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9090770. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32967149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dudek NL, Perlmutter P, Aguilar MI, Croft NP, Purcell AW (2010) Epitope discovery and their use in peptide based vaccines. Curr Pharm Des 16: 3149–3157. - PubMed
-
- Bryson CJ, Jones TD, Baker MP (2010) Prediction of immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins: validity of computational tools. BioDrugs 24: 1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

