The use of inertial sensors system for human motion analysis
- PMID: 23565045
- PMCID: PMC3566464
- DOI: 10.1179/1743288X11Y.0000000006
The use of inertial sensors system for human motion analysis
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this article is to review systematically and appraise critically the literature surrounding the research, comparing inertial sensors with any kind of gold standard; this gold standard has to be a tool for measuring human movement (e.g. electrogoniometry, optoelectronic systems, electromagnetic systems, etc.).
Method: A MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, PEDRo and SCOPUS search of published English language articles was conducted, which focused on articles that compared inertial sensors to any kind of gold standard (e.g. electrogoniometry, optoelectronic systems, electromagnetic systems, etc.), from 2000 to 2010. Two independent reviewers completed the study selection, quality appraisal and data extraction. The Critical Appraisal Skills Programme Español tool was used to assess study quality, and a reliability comparison between the systems was made.
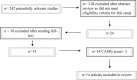
Results: Fourteen out of 242 articles were reviewed, which displayed a similar threat to validity, relating to sample selection and operator blinding. Other study limitations are discussed. A comparison between the different systems showed good agreement across a range of tasks and anatomical regions.
Conclusions: This review concludes that inertial sensors can offer an accurate and reliable method to study human motion, but the degree of accuracy and reliability is site and task specific.
Keywords: Inertial sensors; Motion analysis; Review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Inertial sensors versus standard systems in gait analysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2019 Apr;55(2):265-280. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.18.05306-6. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2019. PMID: 30311493
-
Validity and Reliability of Wearable Sensors for Joint Angle Estimation: A Systematic Review.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Mar 31;19(7):1555. doi: 10.3390/s19071555. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30935116 Free PMC article.
-
The measurement and monitoring of surgical adverse events.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(22):1-194. doi: 10.3310/hta5220. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532239 Review.
-
Wearable inertial sensors in swimming motion analysis: a systematic review.J Sports Sci. 2015;33(7):732-45. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2014.962574. Epub 2014 Oct 30. J Sports Sci. 2015. PMID: 25356682 Review.
Cited by
-
Fetlock Joint Angle Pattern and Range of Motion Quantification Using Two Synchronized Wearable Inertial Sensors per Limb in Sound Horses and Horses with Single Limb Naturally Occurring Lameness.Vet Sci. 2022 Aug 25;9(9):456. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9090456. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36136672 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond timing and step counting in 360° turning-in-place assessment: a scoping review.Biomed Eng Online. 2024 Jan 31;23(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12938-024-01208-0. Biomed Eng Online. 2024. PMID: 38297359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application-Based Production and Testing of a Core-Sheath Fiber Strain Sensor for Wearable Electronics: Feasibility Study of Using the Sensors in Measuring Tri-Axial Trunk Motion Angles.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Oct 3;19(19):4288. doi: 10.3390/s19194288. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31623321 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of 3D Knee Kinematics during Gait on Treadmill with an Instrumented Knee Brace.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 6;23(4):1812. doi: 10.3390/s23041812. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36850411 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Tridimensional Shoulder Kinematics between Asymptomatic Subjects and Subjects Suffering from Rotator Cuff Tears by Means of Inertial Sensors: A Cross-Sectional Study.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 16;23(2):1012. doi: 10.3390/s23021012. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mills PM, Morrison S, Lloyd DG, Barret RS. Repeatability of 3D gait kinematics obtained from an electromagnetic tracking system during treadmill locomotion. J Biomech. 1996;40:1504–11. - PubMed
-
- Burnett AF, Barret CJ, Marshall RN, Elliot BC, Day RE. Three dimensional measurement of lumbar spine kinematics for fast bowlers in cricket. Clin Biomech. 1998;13:574–83. - PubMed
-
- Mannion A, Troke M. A comparison of two motion analysis systems used in the measurement of lumbar spinal mobility. Clin Biomech. 1999;14:612–19. - PubMed
-
- Luinge HJ, Veltink PH. Measuring orientation of human body segments using miniature gyroscopes and accelerometers. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2005;43:273–82. - PubMed
-
- Goodvin C, Edward J, Huang K, Sakaki K. Development of a real-time three-dimensional spinal motion measurement system for clinical practice. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2006;44:1061–75. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources