Conserved function of lincRNAs in vertebrate embryonic development despite rapid sequence evolution
- PMID: 22196729
- PMCID: PMC3376356
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.055
Conserved function of lincRNAs in vertebrate embryonic development despite rapid sequence evolution
Erratum in
- Cell. 2012 Oct 26;151(3):684-6
Abstract
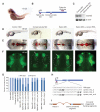
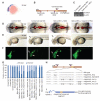
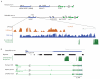
Thousands of long intervening noncoding RNAs (lincRNAs) have been identified in mammals. To better understand the evolution and functions of these enigmatic RNAs, we used chromatin marks, poly(A)-site mapping and RNA-Seq data to identify more than 550 distinct lincRNAs in zebrafish. Although these shared many characteristics with mammalian lincRNAs, only 29 had detectable sequence similarity with putative mammalian orthologs, typically restricted to a single short region of high conservation. Other lincRNAs had conserved genomic locations without detectable sequence conservation. Antisense reagents targeting conserved regions of two zebrafish lincRNAs caused developmental defects. Reagents targeting splice sites caused the same defects and were rescued by adding either the mature lincRNA or its human or mouse ortholog. Our study provides a roadmap for identification and analysis of lincRNAs in model organisms and shows that lincRNAs play crucial biological roles during embryonic development with functionality conserved despite limited sequence conservation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic identification of long noncoding RNAs expressed during zebrafish embryogenesis.Genome Res. 2012 Mar;22(3):577-91. doi: 10.1101/gr.133009.111. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22110045 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic identification and characterization of cardiac long intergenic noncoding RNAs in zebrafish.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 28;7(1):1250. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00823-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28455512 Free PMC article.
-
Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jul 14;106(28):11667-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904715106. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19571010 Free PMC article.
-
lincRNAs: genomics, evolution, and mechanisms.Cell. 2013 Jul 3;154(1):26-46. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.020. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23827673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The four dimensions of noncoding RNA conservation.Trends Genet. 2014 Apr;30(4):121-3. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Mar 7. Trends Genet. 2014. PMID: 24613441 Review.
Cited by
-
A Genomic Analysis of Factors Driving lincRNA Diversification: Lessons from Plants.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Sep 8;6(9):2881-91. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.030338. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 27440919 Free PMC article.
-
Computational prediction and experimental validation identify functionally conserved lncRNAs from zebrafish to human.Nat Genet. 2024 Jan;56(1):124-135. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01620-7. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 38195860 Free PMC article.
-
Pontin functions as an essential coactivator for Oct4-dependent lincRNA expression in mouse embryonic stem cells.Nat Commun. 2015 Apr 10;6:6810. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7810. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25857206 Free PMC article.
-
LIMT is a novel metastasis inhibiting lncRNA suppressed by EGF and downregulated in aggressive breast cancer.EMBO Mol Med. 2016 Sep 1;8(9):1052-64. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201606198. Print 2016 Sep. EMBO Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27485121 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted chromosomal deletions and inversions in zebrafish.Genome Res. 2013 Jun;23(6):1008-17. doi: 10.1101/gr.154070.112. Epub 2013 Mar 11. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23478401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
-
- Bertone P, Stolc V, Royce TE, Rozowsky JS, Urban AE, Zhu X, Rinn JL, Tongprasit W, Samanta M, Weissman S, et al. Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science. 2004;306:2242–2246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

