Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged polymeric nanoparticles as a biomimetic delivery platform
- PMID: 21690347
- PMCID: PMC3131364
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1106634108
Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged polymeric nanoparticles as a biomimetic delivery platform
Abstract
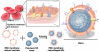
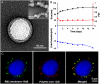
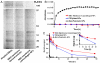
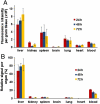
Efforts to extend nanoparticle residence time in vivo have inspired many strategies in particle surface modifications to bypass macrophage uptake and systemic clearance. Here we report a top-down biomimetic approach in particle functionalization by coating biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles with natural erythrocyte membranes, including both membrane lipids and associated membrane proteins for long-circulating cargo delivery. The structure, size and surface zeta potential, and protein contents of the erythrocyte membrane-coated nanoparticles were verified using transmission electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering, and gel electrophoresis, respectively. Mice injections with fluorophore-loaded nanoparticles revealed superior circulation half-life by the erythrocyte-mimicking nanoparticles as compared to control particles coated with the state-of-the-art synthetic stealth materials. Biodistribution study revealed significant particle retention in the blood 72 h following the particle injection. The translocation of natural cellular membranes, their associated proteins, and the corresponding functionalities to the surface of synthetic particles represents a unique approach in nanoparticle functionalization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Size Dependency of Circulation and Biodistribution of Biomimetic Nanoparticles: Red Blood Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles.Cells. 2019 Aug 13;8(8):881. doi: 10.3390/cells8080881. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31412631 Free PMC article.
-
'Marker-of-self' functionalization of nanoscale particles through a top-down cellular membrane coating approach.Nanoscale. 2013 Apr 7;5(7):2664-8. doi: 10.1039/c3nr00015j. Nanoscale. 2013. PMID: 23462967 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles combined with low-dose irradiation: a new approach to enhance drug targeting in gastric cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Mar 17;12:2129-2142. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S126016. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28360520 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: A multifunctional biomimetic platform for cancer diagnosis and therapy.Acta Biomater. 2020 Aug;112:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.05.028. Epub 2020 May 26. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32470527 Review.
-
Biodegradable polymeric nanocarriers for pulmonary drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008 Jun;5(6):629-39. doi: 10.1517/17425247.5.6.629. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008. PMID: 18532919 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of targeted drug delivery by cell membrane-based biomimetic nanoparticles for inflammatory diseases and cancers.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Oct 30;29(1):523. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02124-8. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39472940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Basic Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Oct 7;16(10):1306. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101306. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microenvironment-responsive nanomedicines: a promising direction for tissue regeneration.Mil Med Res. 2024 Oct 21;11(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00573-0. Mil Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39434177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-pathogenic Trojan horse Nissle1917 triggers mitophagy through PINK1/Parkin pathway to discourage colon cancer.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Sep 27;29:101273. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101273. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39415764 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted blood-brain barrier penetration and precise imaging of infiltrative glioblastoma margins using hybrid cell membrane-coated ICG liposomes.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Oct 5;22(1):603. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02870-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39367395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC. Long-circulating and target-specific nanoparticles: Theory to practice. Pharmacol Rev. 2001;53:283–318. - PubMed
-
- Davis ME, Chen ZG, Shin DM. Nanoparticle therapeutics: An emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:771–782. - PubMed
-
- Peer D, et al. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2:751–760. - PubMed
-
- Yoo JW, Chambers E, Mitragotri S. Factors that control the circulation time of nanoparticles in blood: Challenges, solutions and future prospects. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16:2298–2307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

