Wide Tuning Range Wavelength-Swept Laser With Two Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers
- PMID: 20651947
- PMCID: PMC2907922
- DOI: 10.1109/LPT.2004.841003
Wide Tuning Range Wavelength-Swept Laser With Two Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers
Abstract
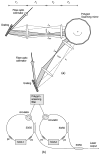
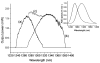
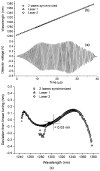
We demonstrate a wide tuning range high-speed wavelength-swept semiconductor laser based on a polygon scanning filter that is common to two laser cavities. Linear wavelength tuning was achieved over 145 nm around 1310 nm at a tuning repetition rate of 20 kHz. The wavelength tuning filter is expandable to accommodate multiple semiconductor optical amplifiers for further widening of the laser wavelength tuning range.
Figures
Similar articles
-
115 kHz tuning repetition rate ultrahigh-speed wavelength-swept semiconductor laser.Opt Lett. 2005 Dec 1;30(23):3159-61. doi: 10.1364/ol.30.003159. Opt Lett. 2005. PMID: 16350273 Free PMC article.
-
High-speed wavelength-swept semiconductor laser with a polygon-scanner-based wavelength filter.Opt Lett. 2003 Oct 15;28(20):1981-3. doi: 10.1364/ol.28.001981. Opt Lett. 2003. PMID: 14587796
-
Fast and wide tuning range wavelength-swept fiber laser based on dispersion tuning and its application to dynamic FBG sensing.Opt Express. 2009 May 11;17(10):8310-8. doi: 10.1364/oe.17.008310. Opt Express. 2009. PMID: 19434164
-
High-power wavelength-swept laser in Littman telescope-less polygon filter and dual-amplifier configuration for multichannel optical coherence tomography.Opt Lett. 2009 Sep 15;34(18):2814-6. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.002814. Opt Lett. 2009. PMID: 19756114
-
Wide tuning range wavelength-swept laser with a single SOA at 1020 nm for ultrahigh resolution Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography.Opt Express. 2011 Oct 24;19(22):21227-37. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.021227. Opt Express. 2011. PMID: 22108975
Cited by
-
Identifying intestinal metaplasia at the squamocolumnar junction by using optical coherence tomography.Gastrointest Endosc. 2007 Jan;65(1):50-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2006.04.027. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007. PMID: 17137858 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase stable swept-source optical coherence tomography with active mode-locking laser for contrast enhancements of retinal angiography.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 17;11(1):16636. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95982-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34404853 Free PMC article.
-
Phase-resolved optical frequency domain imaging.Opt Express. 2005 Jul 11;13(14):5483-93. doi: 10.1364/opex.13.005483. Opt Express. 2005. PMID: 19498543 Free PMC article.
-
115 kHz tuning repetition rate ultrahigh-speed wavelength-swept semiconductor laser.Opt Lett. 2005 Dec 1;30(23):3159-61. doi: 10.1364/ol.30.003159. Opt Lett. 2005. PMID: 16350273 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-spectral laser speckle contrast images using a wavelength-swept laser.J Biomed Opt. 2019 Jul;24(7):1-9. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.7.076001. J Biomed Opt. 2019. PMID: 31290292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wysocki PF, Digonnet MJ, Kim BY. Broad-spectrum, wavelength-swept, erbium-doped fiber laser at 1.55 μm. Opt Lett. 1990;15:879–881. - PubMed
-
- Harvey KC, Myatt CJ. External-cavity diode laser using a grazing-incidence diffraction grating. Opt Lett. 1991;16:910–912. - PubMed
-
- Yun SH, Boudoux C, Tearney GJ, Bouma BE. High-speed wavelength-swept semiconductor laser with a polygon-scanner-based wavelength filter. Opt Lett. 2003;28:1981–1983. - PubMed
-
- Yun SH, Richardson DJ, Culverhouse DO, Kim BY. Wavelength-swept fiber laser with frequency shifted feedback and resonantly swept intracavity acoustooptic tunable filter. IEEE J Sel Topics Quantum Electron. 1997 Aug;3(8):1087–1096.
-
- Eickhoff W, Ulrich R. Optical frequency domain reflectometry in single-mode fiber. Appl Phys Lett. 1981;39:693–695.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
