Clinical significance of elongation factor-1 delta mRNA expression in oesophageal carcinoma
- PMID: 15199388
- PMCID: PMC2409802
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601941
Clinical significance of elongation factor-1 delta mRNA expression in oesophageal carcinoma
Abstract
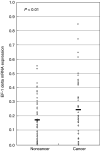
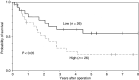
Elongation factor-1 (EF-1) delta is a subunit of EF-1, which is a protein complex that participates in the elongation step of mRNA translation and has recently been considered to correlate with oncogenic transformation. However, there has been no information regarding the clinical significance of EF-1 delta mRNA expression in malignant tumours, including oesophageal carcinoma. Thus, we quantitated the expression of EF-1 delta in malignant and benign oesophageal tissues and associated these levels with clinicopathologic parameters of oesophageal carcinoma. Paired oesophageal tissue samples from cancerous and corresponding noncancerous parts were obtained from 52 patients who underwent curative oesophagectomy. Quantitative analyses of EF-1 delta expression were performed using real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Elongation factor-1 delta mRNA overexpression in cancerous tissues compared to normal counterparts was observed in 38 of 52 (73%) patients. The mean expression level of EF-1 delta mRNA in cancerous tissues was significantly higher than that in noncancerous tissues (P<0.01). A higher expression of EF-1 delta was significantly correlated with lymph node metastases (P<0.05) and advanced stages (P<0.05). Furthermore, the cause-specific survival of patients with a higher expression of EF-1 delta was significantly poorer than those with a lower expression (5-year cause-specific survival rates; 23 and 54%, respectively, P<0.05). The results of this study indicated that EF-1 delta mRNA expression was significantly higher in cancerous compared to noncancerous oesophageal tissues, and a higher expression of EF-1 delta mRNA was correlated with lymph node metastases, advanced disease stages and poorer prognosis for patients with oesophageal carcinoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduced stratifin expression can serve as an independent prognostic factor for poor survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Dig Dis Sci. 2010 Sep;55(9):2552-60. doi: 10.1007/s10620-009-1065-0. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Dig Dis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20108042
-
survivin messenger RNA expression is a good prognostic biomarker for oesophageal carcinoma.Br J Cancer. 2002 Oct 7;87(8):883-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600546. Br J Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12373603 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of Twist in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with neoplastic transformation and distant metastasis.J Clin Pathol. 2007 May;60(5):510-4. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2006.039099. Epub 2006 Jul 5. J Clin Pathol. 2007. PMID: 16822877 Free PMC article.
-
Contactin-1 (CNTN-1) overexpression is correlated with advanced clinical stage and lymph node metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jul;42(7):612-8. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hys066. Epub 2012 May 11. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22581910
-
Clinical and prognostic significance of RhoA and RhoC gene expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2007 Dec;14(12):3593-601. doi: 10.1245/s10434-007-9562-x. Epub 2007 Sep 25. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17896152
Cited by
-
Fasting to enhance Cancer treatment in models: the next steps.J Biomed Sci. 2020 May 5;27(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00651-0. J Biomed Sci. 2020. PMID: 32370764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Investigation to Identify Anticancer Targets of Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom in Human Hepatocarcinoma HepG2 Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2018 May 10;10(5):194. doi: 10.3390/toxins10050194. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29748501 Free PMC article.
-
Fluvastatin mediated breast cancer cell death: a proteomic approach to identify differentially regulated proteins in MDA-MB-231 cells.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 30;9(9):e108890. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108890. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25268751 Free PMC article.
-
Independent overexpression of the subunits of translation elongation factor complex eEF1H in human lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 3;14:913. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-913. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25472873 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and biological significance of mitotic centromere-associated kinesin overexpression in human gastric cancer.Br J Cancer. 2007 Aug 20;97(4):543-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603905. Epub 2007 Jul 24. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17653072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anand N, Murthy S, Amann G, Wernick M, Porter LA, Cukier H, Collins C, Gray JW, Demetrick DJ, Lee JM (2002) Gene encoding protein elongation factor EEF1A2 is a putative oncogene in ovarian cancer. Nat Genet 31: 301–305 - PubMed
-
- Bieche I, Olivi M, Champeme MH, Vidaud D, Lidereau R, Vidaud M (1998) Novel approach to quantitative polymerase chain reaction using real-time detection: application to the detection of gene amplification in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 78: 661–666 - PubMed
-
- Bieche I, Onody P, Laurendeau I, Olivi M, Vidaud D, lidereau R, Vidaud M (1999) Real time reverse transcription–PCR assay for future management of ERBB2-based clinical applications. Clin Chem 45: 1148–1156 - PubMed
-
- Buckhaults P, Rago C, St Croix B, Romans KE, Saha S, Zhang L, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (2001) Secreted and cell surface genes expressed in benign and malignant colorectal tumors. Cancer Res 61: 6996–7001 - PubMed
-
- Chi K, Jones DV, Frazier ML (1992) Expression of an elongation factor 1 gamma-related sequence in adenocarcinomas of the colon. Gastroenterology 103: 98–102 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

