Estrogen receptor transcription and transactivation: Structure-function relationship in DNA- and ligand-binding domains of estrogen receptors
- PMID: 11250728
- PMCID: PMC138657
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr80
Estrogen receptor transcription and transactivation: Structure-function relationship in DNA- and ligand-binding domains of estrogen receptors
Abstract
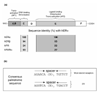
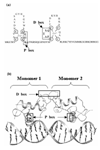
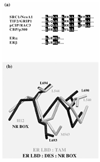
Estrogen receptors are members of the nuclear receptor steroid family that exhibit specific structural features, ligand-binding domain sequence identity and dimeric interactions, that single them out. The crystal structures of their DNA-binding domains give some insight into how nuclear receptors discriminate between DNA response elements. The various ligand-binding domain crystal structures of the two known estrogen receptor isotypes (alpha and beta) allow one to interpret ligand specificity and reveal the interactions responsible for stabilizing the activation helix H12 in the agonist and antagonist positions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The analysis of chimeric human/rainbow trout estrogen receptors reveals amino acid residues outside of P- and D-boxes important for the transactivation function.Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jul 15;28(14):2634-42. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.14.2634. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 10908317 Free PMC article.
-
Function of N-terminal transactivation domain of the estrogen receptor requires a potential alpha-helical structure and is negatively regulated by the A domain.Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Nov;14(11):1849-71. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.11.0546. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 11075817
-
Identification of amino acids in the hormone binding domain of the human estrogen receptor important in estrogen binding.J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 16;271(33):20053-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.33.20053. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8702724
-
Homology modelling of the nuclear receptors: human oestrogen receptorbeta (hERbeta), the human pregnane-X-receptor (PXR), the Ah receptor (AhR) and the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) ligand binding domains from the human oestrogen receptor alpha (hERalpha) crystal structure, and the human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) ligand binding domain from the human PPARgamma crystal structure.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Feb;84(2-3):117-32. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(03)00021-9. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12710995 Review.
-
Ligand-binding domain of estrogen receptors.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1999 Dec;10(6):550-6. doi: 10.1016/s0958-1669(99)00034-8. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1999. PMID: 10600690 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased frequency of ESR1 mutation in metastatic breast cancer by dosing selective estrogen receptor modulator followed by aromatase inhibitor.Oncol Lett. 2020 Aug;20(2):1231-1238. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11669. Epub 2020 May 22. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32724363 Free PMC article.
-
Human Estrogen Receptor Alpha Antagonists, Part 3: 3-D Pharmacophore and 3-D QSAR Guided Brefeldin A Hit-to-Lead Optimization toward New Breast Cancer Suppressants.Molecules. 2022 Apr 28;27(9):2823. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092823. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566172 Free PMC article.
-
Production of unstable proteins through the formation of stable core complexes.Nat Commun. 2016 Mar 17;7:10932. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10932. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26983699 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Assessment for the Estrogenic Effects of Pyrethroid Compounds: Defining the Molecular Initiating Events and Key Events for the Adverse Outcome Pathway.Toxics. 2024 Mar 15;12(3):218. doi: 10.3390/toxics12030218. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 38535951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structurally similar estradiol analogs uniquely alter the regulation of intracellular signaling pathways.J Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Dec 31;50(1):43-57. doi: 10.1530/JME-12-0083. Print 2013 Feb. J Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 23132914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Green S, Walter P, Kumar V, Krust A, Bornert JM, Argos P, Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. . Nature. 1986;320:134–139. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa S, Inoue S, Watanabe T, Hiroi H, Orimo A, Hosoi T, Ouchi Y, Muramatsu M. The complete primary structure of human estrogen receptor beta (hER beta) and its heterodimerization with ER alpha in vivo and in vitro. . Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;243:122–126. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.7893. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuiper GG, Carlsson B, Grandien K, Enmark E, Haggblad J, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA. Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha and beta. . Endocrinology. 1997;138:863–870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

